chem whatarethemechanismsofchemicalchange
Reactivity 3.4.6 - a Lewis acid is an electron-pair acceptor and a Lewis base is an electron-pair donor
Reactivity 3.4.7 - when a Lewis base reacts with a Lewis acid, a coordination bond is formed. nucleophiles are Lewis bases and electrophiles are Lewis acids.
the reaction in which ammonia acts as a base can be represented as:
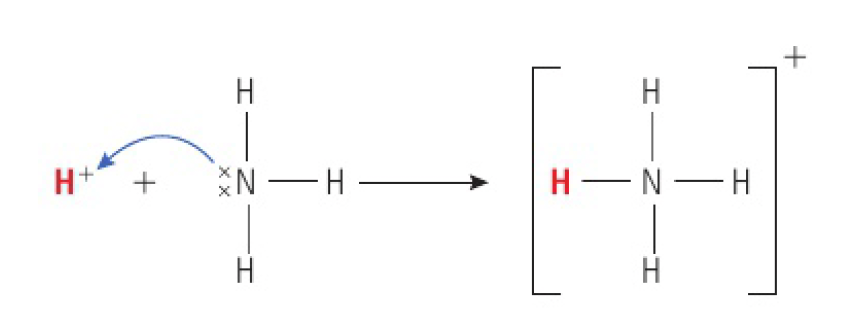
- a acid is a lone pair acceptor
- a Lewis base is a lone pair donor
thus, Lewis bases and Brønsted-Lowry bases are therefore the same group of compounds:
- by either definition, they are species that must have a lone pair of electrons
for Lewis acids, the Lewis definition is broader:
- it is any species capable of accepting a lone pair of electrons
- all Brønsted-Lowry acids are Lewis acids (since
has a vacant orbital) - it also includes molecules that have an incomplete valence shell
Lewis acid-base reactions result in the formation of a covalent bond, which will always be a coordination bond as both electrons come from the base
for example:
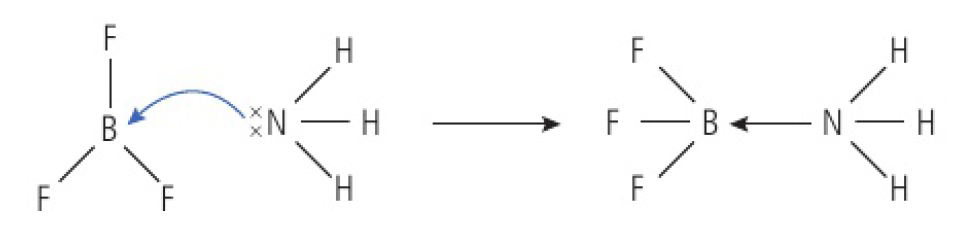
has an incomplete octet, so it can act as a Lewis acid and accept a pair of electrons acts as a Lewis base, donating its lone pair of electrons
Lewis acids are electrophiles and Lewis bases are nucleophiles
-
a nucleophile is electron-rich, and donates a lone pair in bond formation
this is consistent with the definition of Lewis bases -
an electrophile is electron-deficient, and accepts a lone pair in bond formation
this is consistent with the definition of Lewis acids