chem modelsofbondingandstructure
Structure 2.4.6 - condensation polymers form by the reaction between functional groups in each monomer with the release of a small molecule
see 2.4.4 polymers
see 3.2.2 functional groups and classes of compounds
[A][H].[B]O[H]>>[A][B].[H]O[H]monomers with 2 functional groups can be used to make condensation polymers, which can be thought of as “active ends” where condensation reactions can occur.
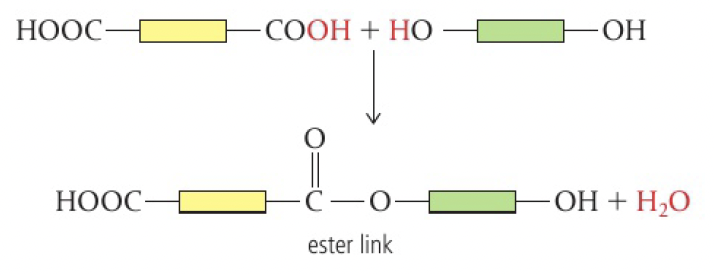
carboxylic acid + alcohol → polyester
when a monomer has two
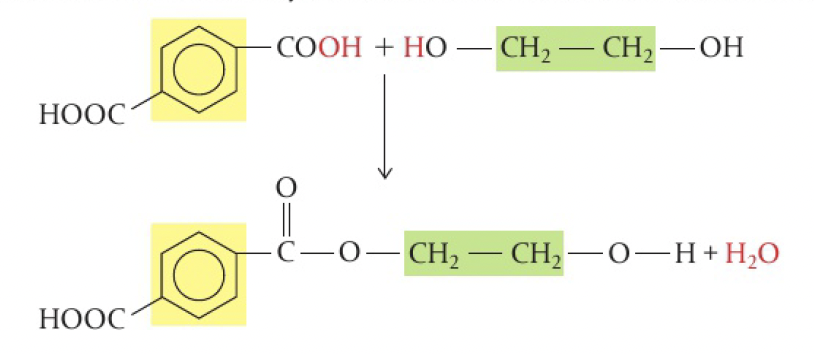
reaction between benzene-1,4-dicarboxylic acid and ethane-1,2-diol
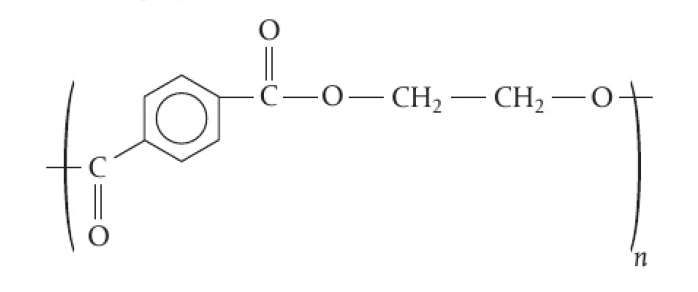
PET - polyethylene terephthalate
carboxylic acid + amine → polyamide
when a monomer has two
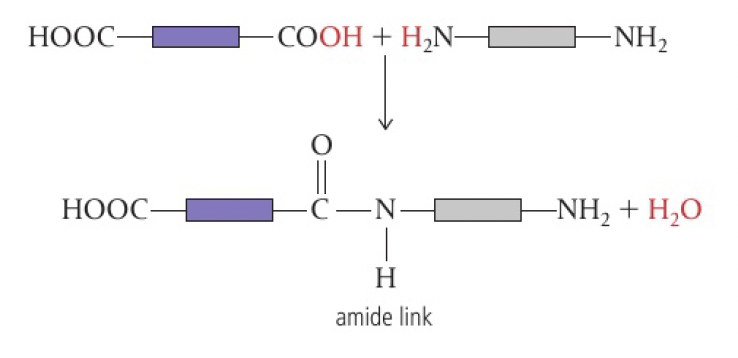
1,6-diaminohexane and hexanedioic acid
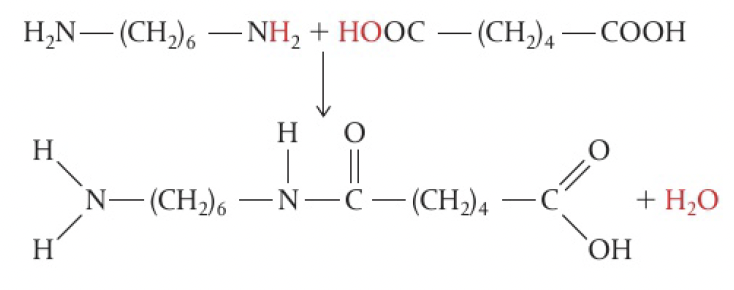
6,6-nylon
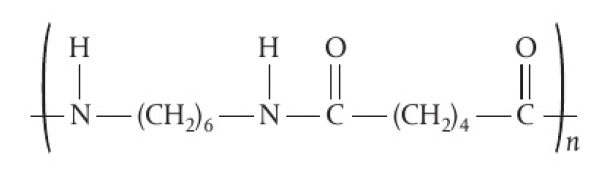
hydrolysis
all biological macromolecules are condensation polymers synthesised in cells by condensation reactions
starch is produced by linking glucose into long chains.
the reverse reaction is known as hydrolysis
hydrolysis reactions occur during digestion, decomposition, and when stored materials need to be mobilised. condensation and hydrolysis reactions are controlled by enzymes (biological catalysts)