chem whatarethemechanismsofchemicalchange
Reactivity 3.2.7 - secondary (rechargeable) cells involve redox reactions that can be reversed using electrical energy
- more expensive but becomes more economical with use
- longer life
lithium ion-battery
benefits from lithium’s:
-
low density
-
high reactivity
-
stores lots of electrical energy per unit mass
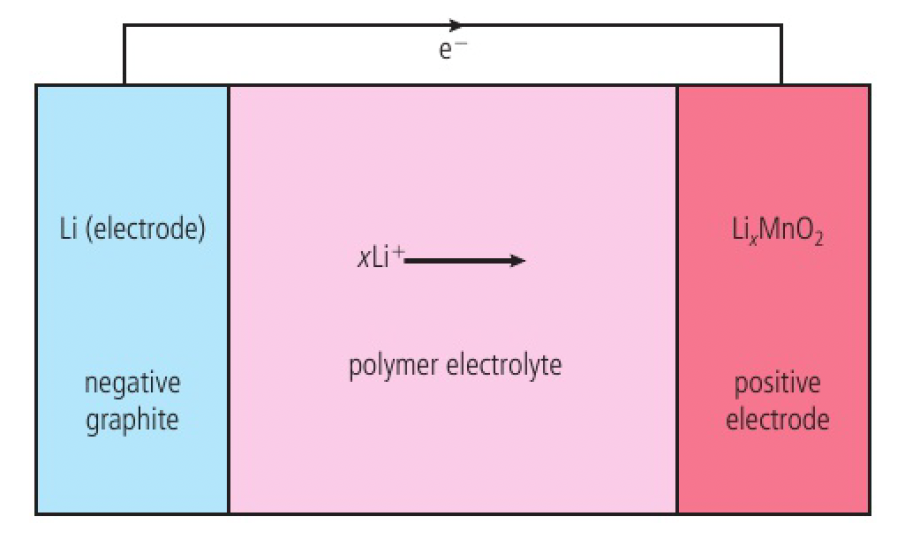
- steps are taken to prevent oxide layer from forming on lithium metal (decrease in contact with electrolyte)
- lithium anode mixed with graphite
- non-aqueous polymer-based electrolyte
- lithium cathode placed in the lattice of a metal oxide
discharging a lithium-ion battery
at the negative electrode, lithium is oxidised:
at the positive electrode, the
the half-reactions are reversed when the battery is recharged.
fuel cells
- since combustion reactions are redox reactions, they can be used to produce an electric current if the reactants are physically separated
the hydrogen fuel cell
negative electrode, anode:
\ce{4H+(aq) +O_{2}(g) +4e- \to 2H_{2}O(l)}
\ce{H_{2}(g) +2OH-(aq)\to 2H_{2}O(l) +2e-}
\ce{H_{2}O(l) +O_{2}(g) +4e- \to 4OH-(aq)}
b) calculate the maximum efficiency of the hydrogen cell when steam is produced instead of water.
plug in values from equation above
c) explain the increased efficiency of a hydrogen-oxygen fuel cell which produces steam compared to water.
the entropy decrease is smaller for the reaction which produces one mole of gaseous water, which leads to a larger efficiency