chem whatarethemechanismsofchemicalchange
Reactivity 3.2.15 - during electrolysis of aqueous solutions, competing reactions can occur at the anode and cathode, including the oxidation and reduction of water
-
the electrolysis of molten salts is different to the electrolysis of aqueous solutions as it is possible for multiple reactions to occur at the anode and cathode
-
with
, sodium metal cannot be produced at the cathode as it would immediately react with water
the reaction at the cathode can be understood in terms of a sequence of two hypothetical steps
thus, water is preferentially reduced to hydrogen
generally, for a solute
- anode: either
or can be oxidised - cathode: either
or can be reduced
selective discharge is the discharge of an ion at the electrode
competing reactions during electrolysis of aqueous solutions
flowchart A[1. identify all the ions present in the electrolyte and determine<br> which will migrate to which electrode] --> B(2. where there is more than one possible reaction at each<br> electrode, write the half-equation for the reaction at each<br> electrode as in the data booklet) --> C[3. the half reaction with the higher electrode potential is the<br>oxidation reaction at the cathode.] --> D[4. the half-reaction with the lower electrode potential is the<br>reduction reaction at the anode.] --> E[5. to deduce the overall equation, balance the electrons lost and<br>gained at the anode and the cathode, then add the two half-<br>equations to write the equation for the net reaction] --> F[6. consider what changes would be observed in the cell as a result<br>of the redox reactions. COBALT? pH?]
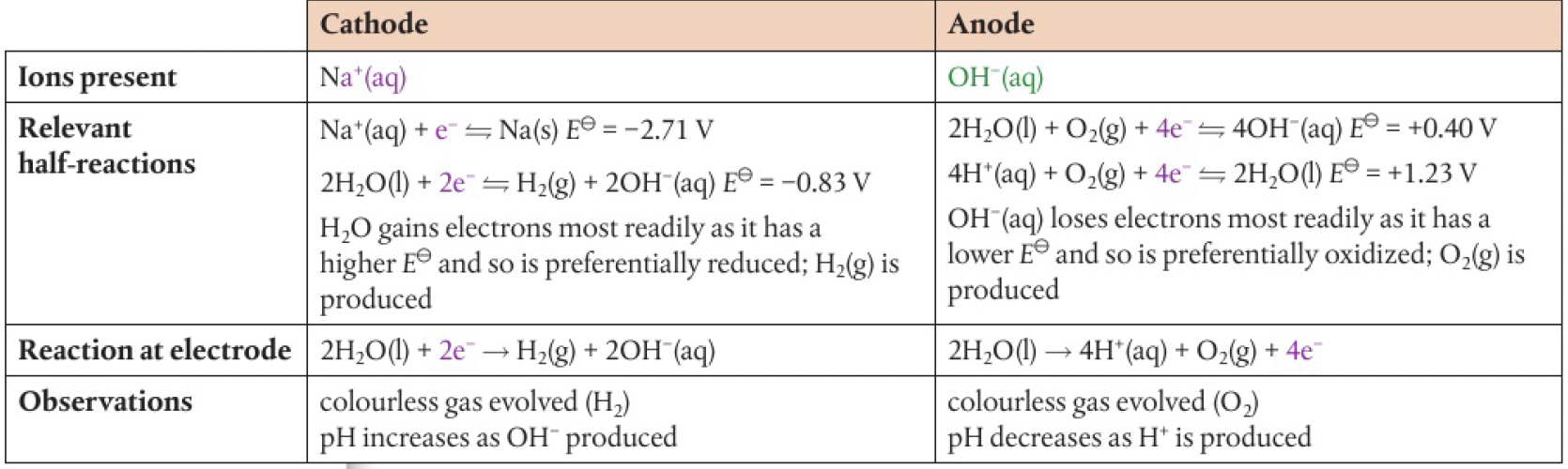
electrolysis of water
since pure water is not a good conductor of electricity, some sulfuric acid or sodium hydroxide is added.
electrolysis of
.png)
overall balanced equation for brine:
the preferential discharge of
electrolysis of
graphite electrodes:
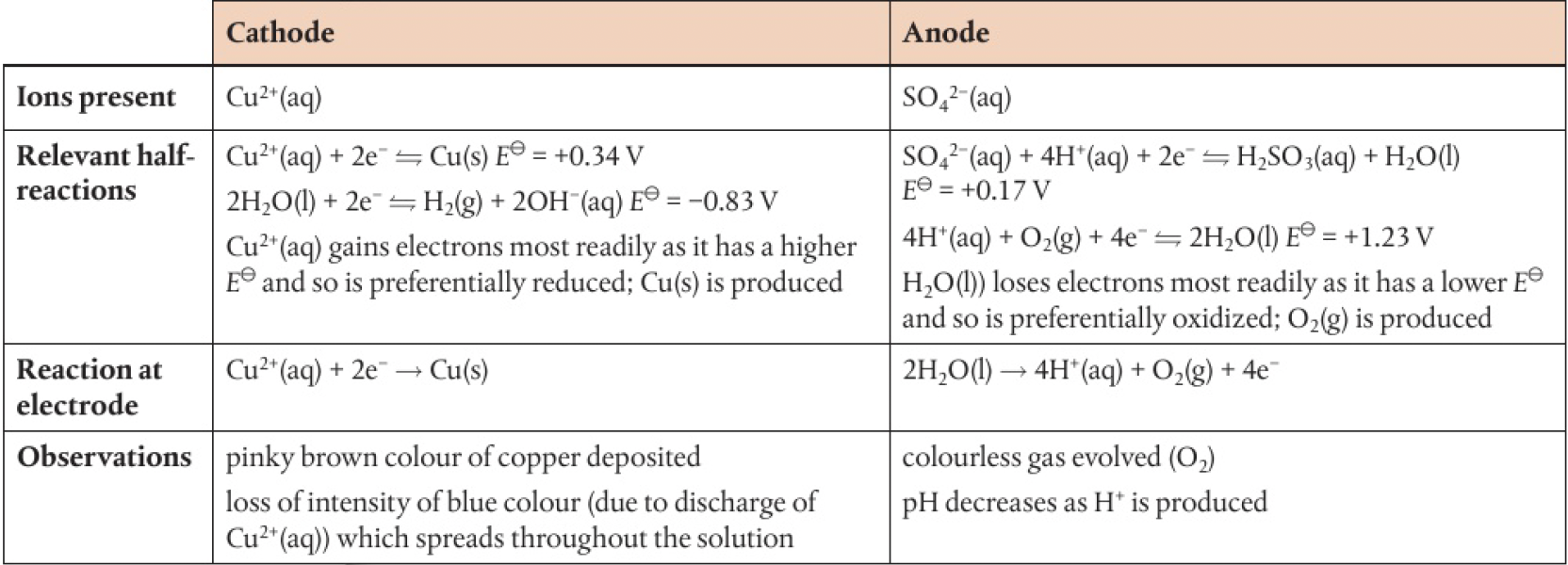
used to precipitate
copper electrodes:
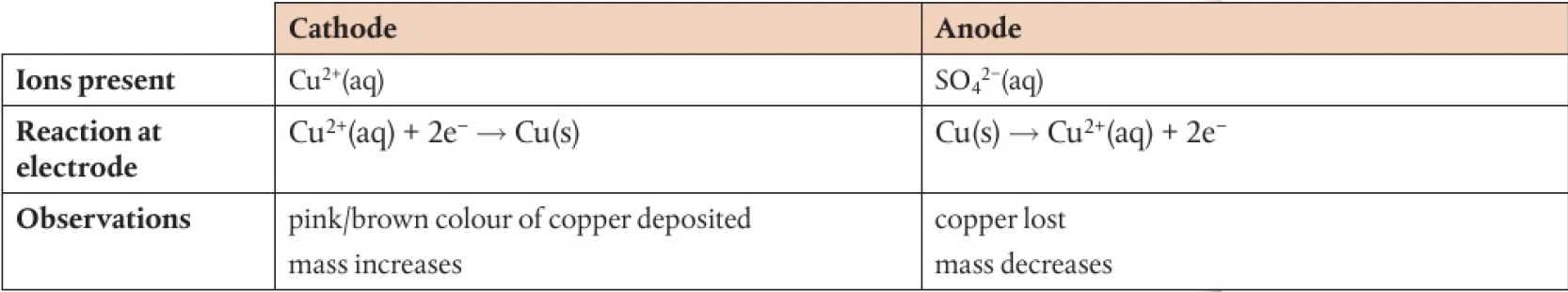
no change in intensity of the blue colour of the solution as
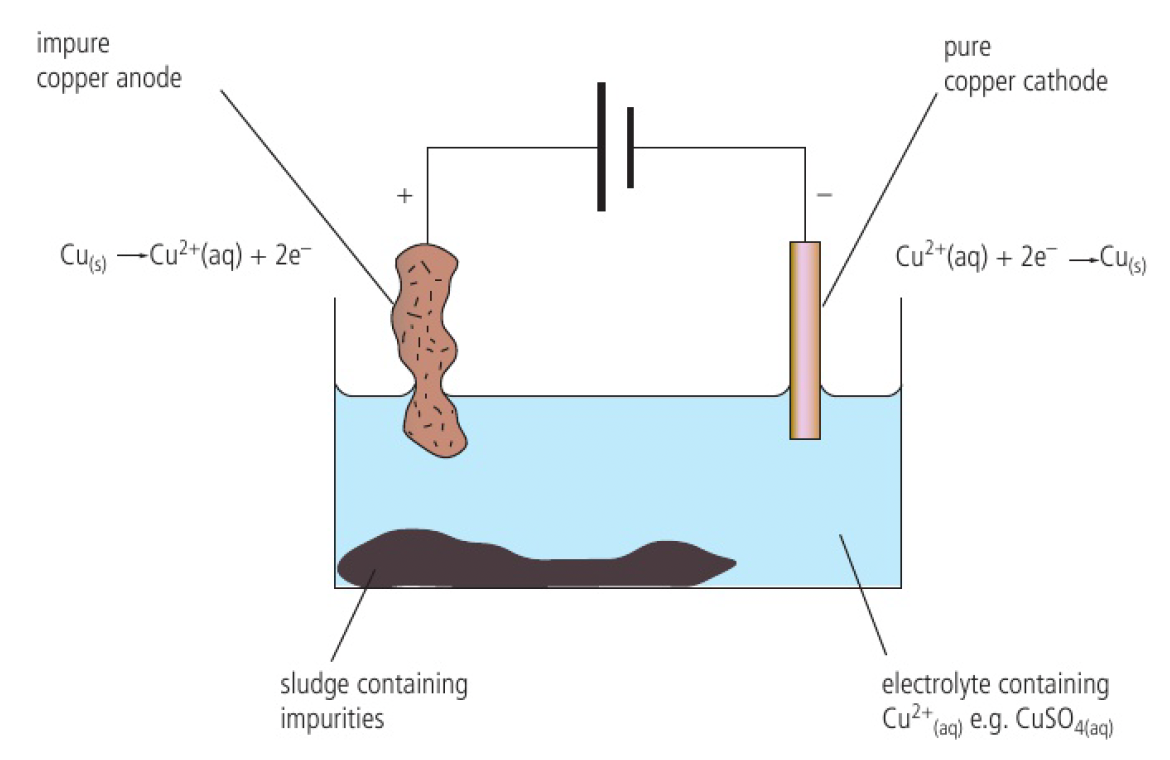
this process can be used to purify copper
- impure copper anode
- small pure copper cathode
- the anode erodes as copper ions are formed and transferred to the cathode
- only copper atoms are formed at the cathode
- the impurities leave the anode as the copper ions are formed and fall to the bottom of the cell