chem whatarethemechanismsofchemicalchange
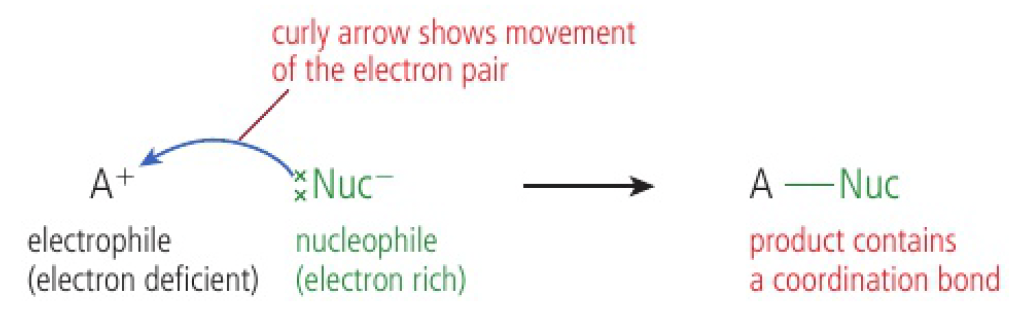
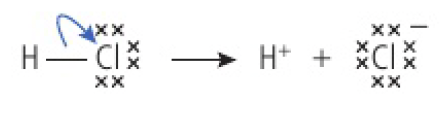
Reactivity 3.4.3 - heterolytic fission is the breakage of a covalent bond when both bonding electrons remain with one of the two fragments formed
- nucleophilic substitution reactions involve heterolytic fission
- one of the products gains both the shared electrons
- the more electronegative atom will gain the negative charge
Example
- the reverse process occurs when a nucleophile donates a pair of electrons to an electrophile