chem modelsofbondingandstructure
Structure 2.4.5 - addition polymers form by the breaking of a double bond in each monomer
see 2.4.4 polymers
addition reactions occur when a multiple bond in a molecule breaks and forms new bonding positions. alkenes and alkynes readily undergo addition reactions, so they can form addition polymers
examples:
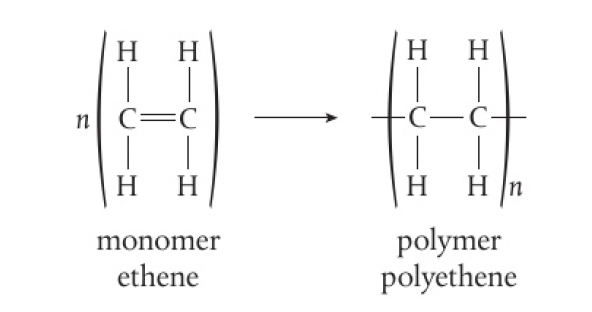
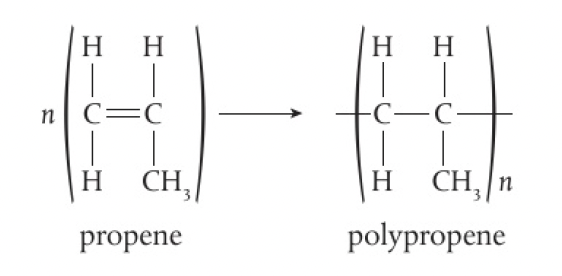
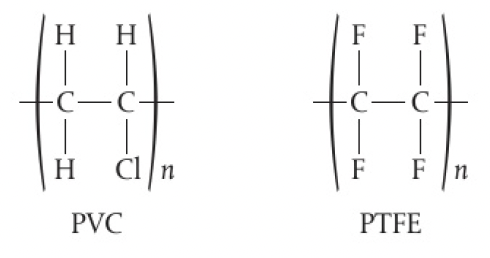
polychloroethene or poly vinyl chloride and polytetrafluoroethene
addition polymerisation reactions do not generate a by-product and so convert 100% of reactants into product. a reaction yield of less than 100% means there is unreacted monomer at the end of the process.
NOTE
lots of polymerisation reactions also use solvents and conditions of high temperature, pressure and/or catalysts, which must be taken into account as part of an environmental assessment of the process
challenge questions
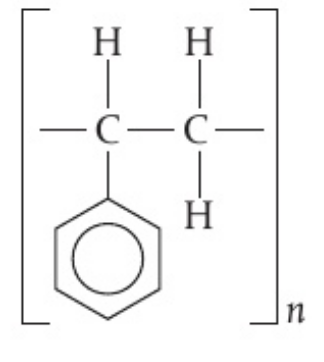
- draw the repeating unit in polystyrene, given that the formula of the monomer is