Reactivity 2.3.6 - the equilibrium law is the basis for quantifying the composition of an equilibrium mixture
calculating the equilibrium constant from equilibrium concentrations
just plug the values into the equilibrium constant expression
calculating the equilibrium constant from initial concentrations
steps:
- write the balanced equation
- under the equation, write in the values of the concentrations of each component using 3 rows: initial, change and equilibrium
- initial represents the concentration originally placed in the flask. unless stated otherwise, the initial product concentration is 0
- change represents the amount that reacts to each equilibrium. a minus sign for reactants represents a decrease in concentration as they are used up, and a plus sign for products represents an increase in concentration as they form. the changes that occur must be in the same ratio as the coefficients in the balanced equation, so if we know one of the change values, we can deduce the others
- equilibrium represents the concentration present in the equilibrium mixture. this can be calculated by applying the amount of change to the initial concentration for each component
- write the expression for
from the balanced equation. substitute the values for equilibrium concentration and calculate
for more complex situations when calculating equilibrium concentrations given

calculations when the equilibrium constant is very small
- when
, the reaction lies far to the left and the equilibrium mixture contains mainly reactants - the change from the initial amount of reactant to the equilibrium amount is close to zero
- therefore the following approximation can also be made:
interesting
the oxidation of
solution
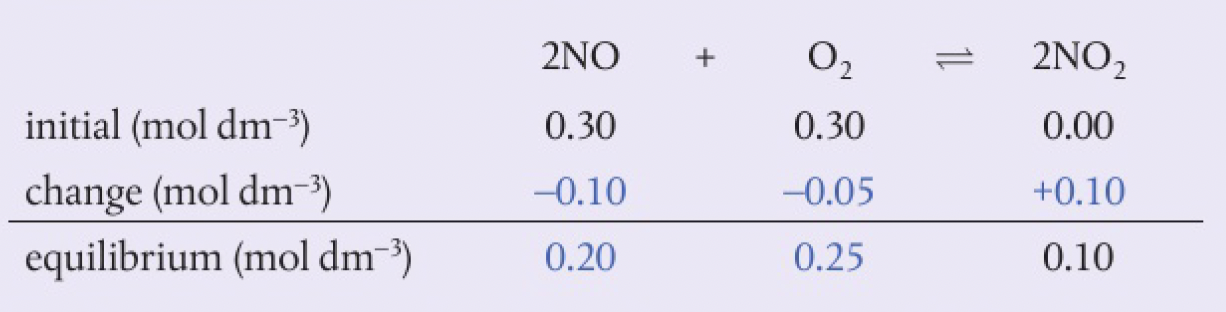
$$
K=\ce{\frac{[NO_{2}]^{2}}{[NO]^{2}[O_{2}]}=\frac{0.10^{2}}{0.20^{2}\times 0.25}=1.0}