chem modelsofparticulatenatureofmatter
Structure 1.4.5 - the molar concentration is determined by the amount of solute and the volume of solution
square brackets are used to represent molar concentration
units of concentration should include
the molar concentration of a solution is based on moles of solute and volume of a solution
solution is a homogenous mixture of two or more substances, which may be solids, liquids, or gases
- the solvent is the component present in the greatest quantity
- the solute is dissolved in the solvent
standard solutions are solutions of known concentration
dilution of a solution
as a solution is diluted, the number of moles of solute remains the same
a serial dilution is a series of dilutions of a standard solution, where the concentration is reduced by a fixed amount at each step. this is done in volumetric flasks.
this can be used in uv-vis spectroscopy, which uses the direct relationship between the concentration and absorbance. the absorbance of each solution is measured and the results plotted as a calibration curve. this curve is then used to determine the unknown concentration of a sample containing the same solute.
challenge questions
- When sodium hydroxide,
, pellets dissolve in water, there is a decrease in the total volume of the solution. Explain what might cause this.
the sodium and hydroxide ions break some hydrogen bonds between the water to form ion-dipole, which are stronger bonds than water and thus shorter, which allows the molecules to pack closer together, reducing the total volume.
- From the shape of the calibration curve in Figure 3, what can you conclude about the relationship between concentration and absorbance at higher concentration? How might this affect the calculation of the unknown concentration?
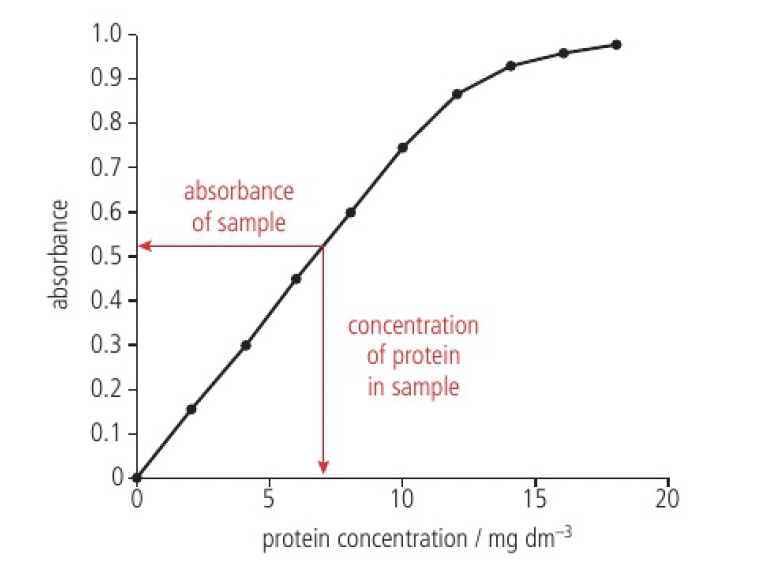
as the concentration gets higher, the absorbance gets closer to 1, which means it becomes opaque and not possible to accurate determine the concentration of solutions with higher concentrations. the relationship also becomes non-linear, so it will be more difficult to determine the calculation of the unknown concentration.