chem whatarethemechanismsofchemicalchange
Reactivity 3.2.16 - electroplating involves the electrolytic coating of an object with a metallic thin layer
electroplating is the process of using electrolysis to deposit a layer of metal on top of another metal or conductive object
an electrolytic cell used for electroplating has the following features:
- the object to be plated (cathode)
- the electrolyte which contains the metal ions which are to coat the object
- the anode (sometimes made of the same plating metal)
- as it is oxidised, it replenishes the ions in the electrolyte which are discharged at the cathode
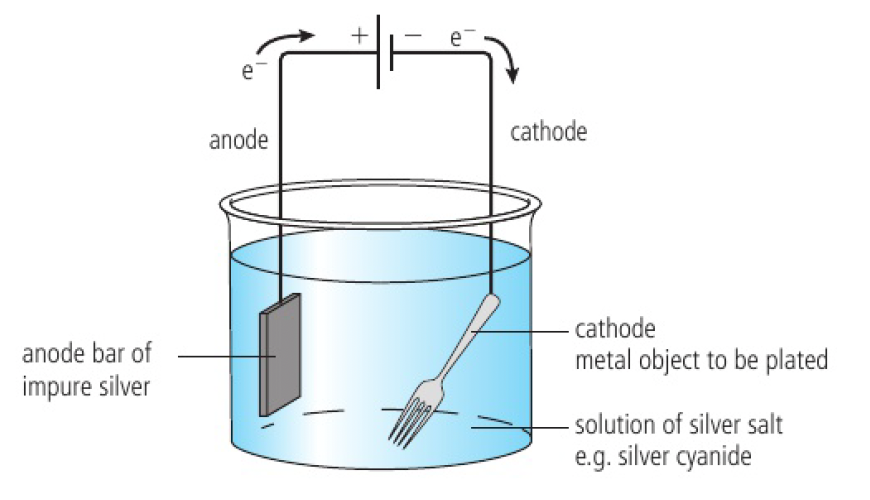
- reduction of the metal ions causes their deposition on the surface of the cathode
- the process can be controlled by altering the current and the time according to how thick a layer of metal is desired
purposes:
- decorative
- corrosion control
- sacrificial protection
- galvanised iron - improvement of function
- with harder wearing materials (ie chromium)