chem whatarethemechanismsofchemicalchange
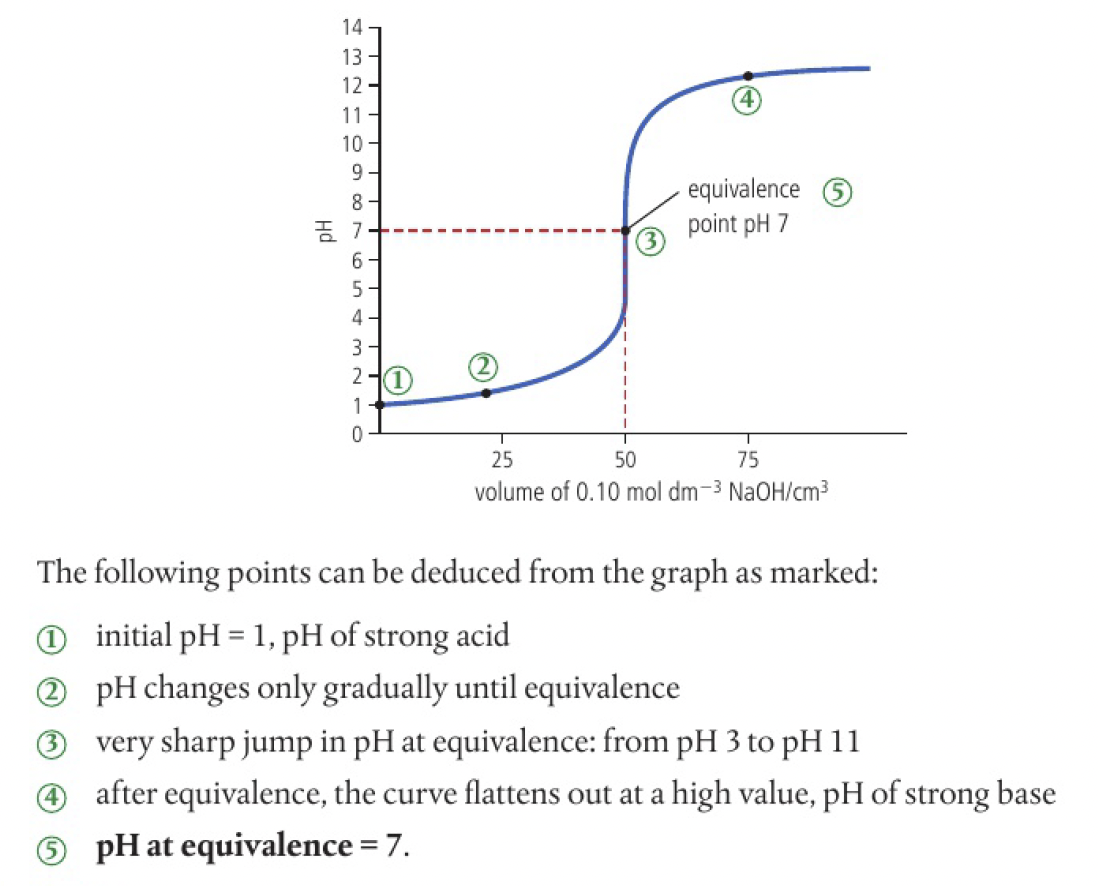
Reactivity 3.1.8 - pH curves for neutralisation reactions involve strong acids and bases have characteristic shapes and features
generation from a titration
acid-base titration is a quantitative technique.
the reaction between an acid and a base takes place in the flask until the equivalence point or stoichiometric point is reached, when the acid and base are present in ratio where both are exactly neutralised.
plotting the
a big jump in
the equivalence point can also be determined using an acid-base indicator
- full dissociation is assumed
- as the titrant is added, neutralisation occurs while excess titrand remains
- as volume changes during addition, this must be taken into account in determining the concentration