chem modelsofbondingandstructure
Structure 2.2.14 - formal charge values can be calculated for each atom in a species and used to determine which of several possible Lewis formulas is preferred
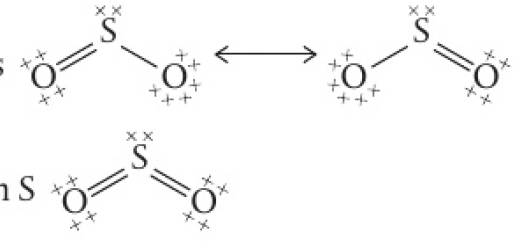
formal charge can be used to determine the most stable structure out of possible resonance structures
formal charge treats covalent bonds as if they were purely covalent with equal electron distribution
so a single bond means 2 electrons are shared, and thus 1 electron per atom
low formal charges mean that less charge transfer has taken place, representing the most stable or preferred structure.
this can now be applied to the 3 different Lewis formulas for
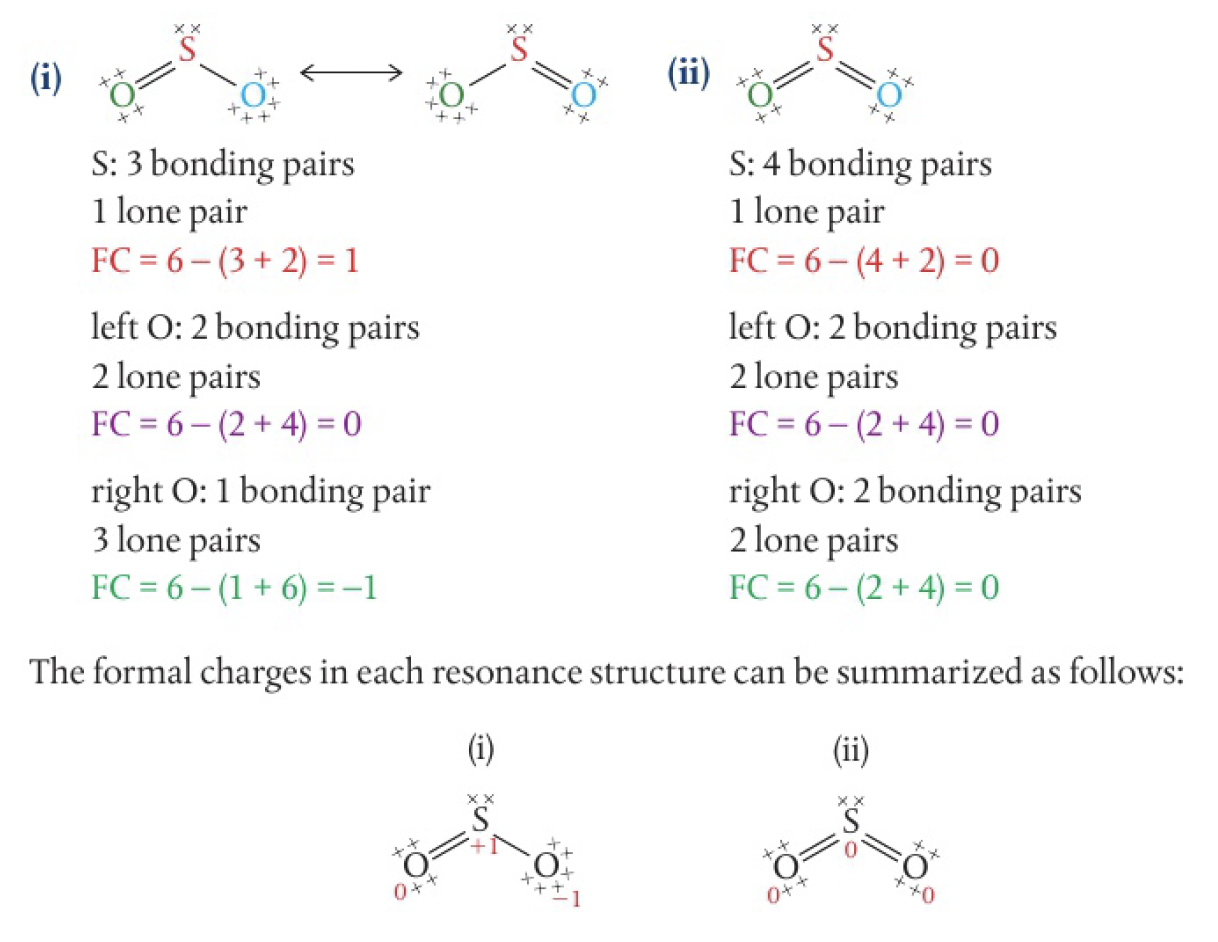
note that the sum of the formal charges for a species must be zero for a neutral molecule, or equal to the charge on an ion.
since formal charge ignores electronegativity values, it does not give the full picture.
a useful guideline to follow is that the most stable of several Lewis formulas is the structure that has:
- the lowest formal charges and
- negative values formal charges on the more electronegative atoms
eg
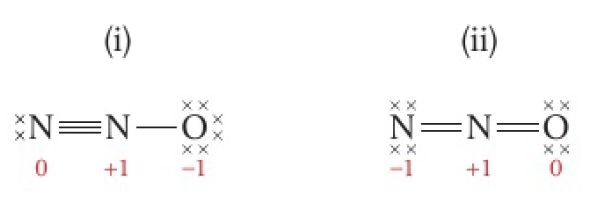
(i) would be more stable and the preferred structure since
challenge questions
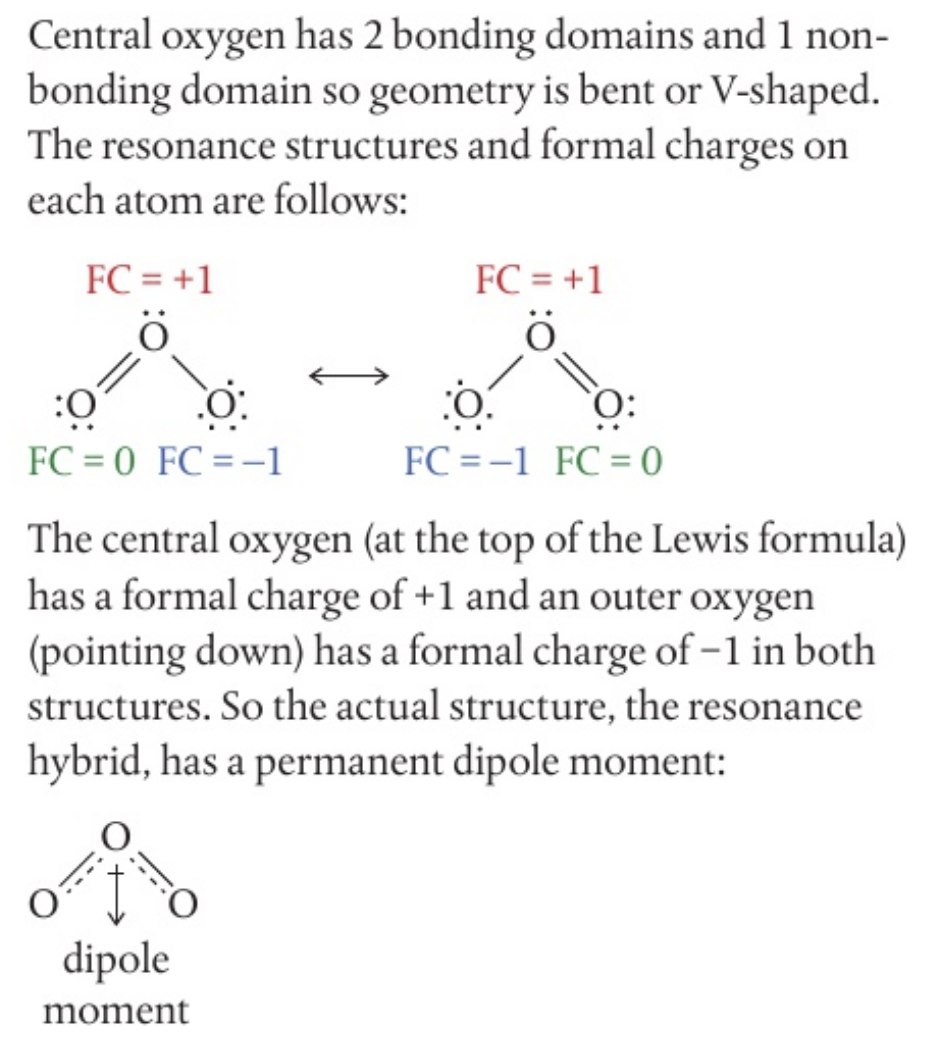
- although ozone,
contains three identical atoms, it is a polar molecule. can you explain why by considering the geometry, resonance structures and formal charge?
- there are several covalently bonded molecules and ions that contain transition metals, such as
and . what problems arise in determining the formal charge of species like these?
the number of valence electrons of transition metals varies. the formal charge model may not be as useful for complex ions, as the values obtained do not make much sense.