Reactivity 2.2.2 species react as a result of collisions of sufficient energy and proper orientation
- particles in a substance move randomly as a result of the kinetic energy they possess
- not all particles in a substance at one time will have the same values of kinetic energy
the average of these values is directly related to its absolute temperature
increasing temperature means increasing the average kinetic energy.
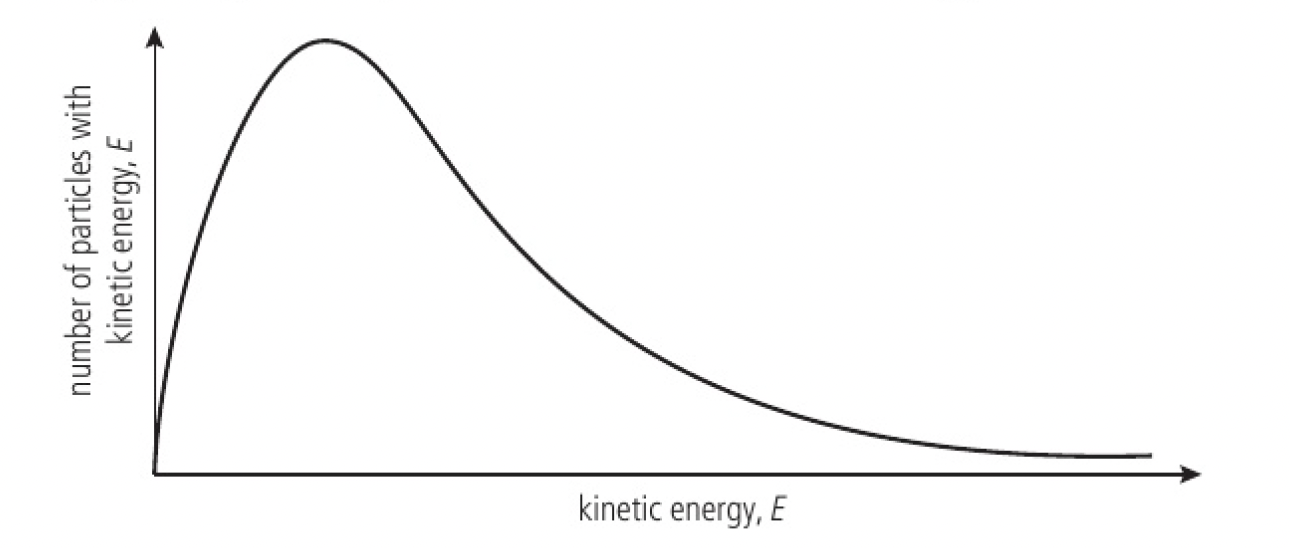
- the Maxwell-Boltzmann energy distribution curve shows the fact that particles in a gas at a specific temperature show a range in their values of kinetic energies
- the area under the curve represents the total number of particles in the sample
collisions between particles
-
when reactants are placed together, the kinetic energy that their particles possess causes them to collide
-
the energy of these collisions may result in some bonds within the reactants being broken, and some new bonds forming
-
as a result, products form and the reaction ‘happens’
-
the rate of a reaction depends on the frequency of collisions that occur between particles possessing both values of kinetic energy greater than the activation energy and appropriate collision geometry
not all collisions will be successful
there are two main factors that influence the success of a collision:
- the energy of the collision and
- the geometry of the collision
energy of collision
-
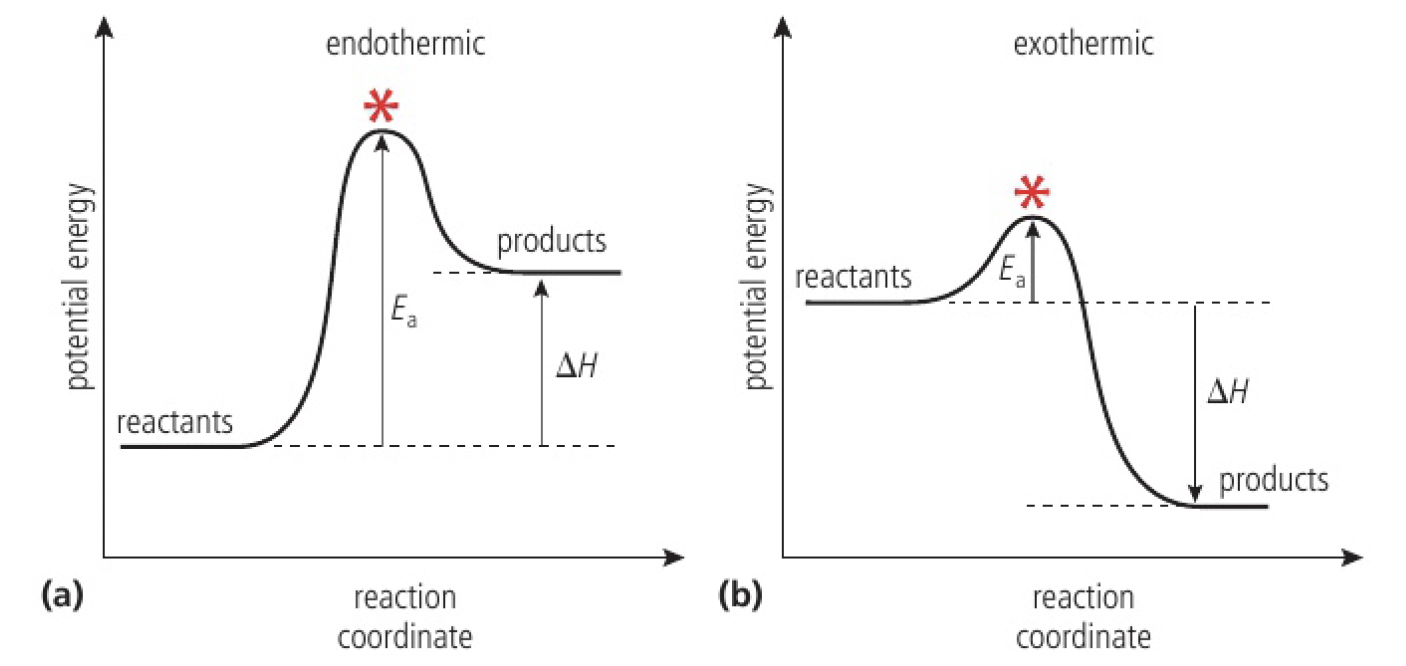
for a collision to lead to a reaction, the particles must have a certain minimum value for their kinetic energy, known as the activation energy,
-
the activation energy is necessary for overcoming repulsion and breaking some bonds in the reactants before they can react
- when the activation energy is supplied, the reactants achieve the transition state from which products can form
- below the activation energy, particles do not react, but will still collide
-
the magnitude of the activation energy will vary from one reaction to another
-
generally, high activation energy reactions proceed slower than those with low activation energy as fewer particles will have the required energy
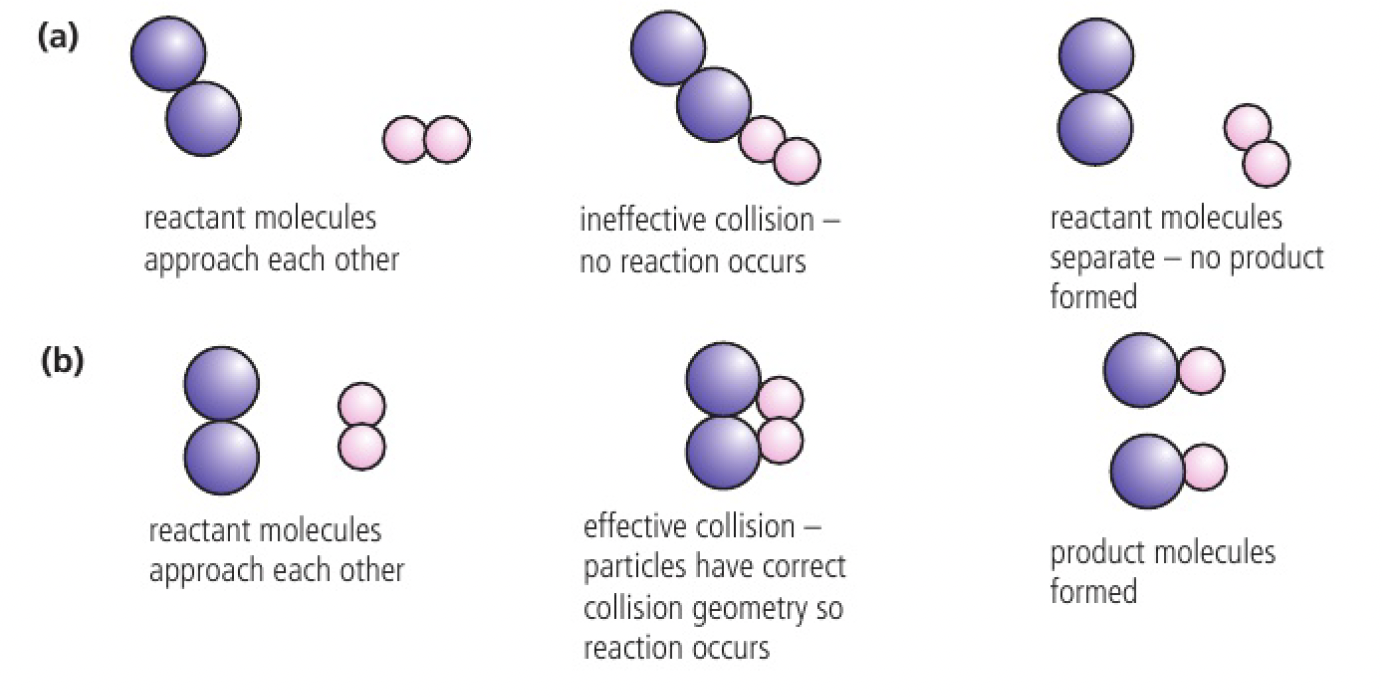
geometry of collision
- particles can collide in many different orientations because collisions are random
- in some reactions, this determines whether or not the collisions will be successful