chem whatdriveschemicalreactions
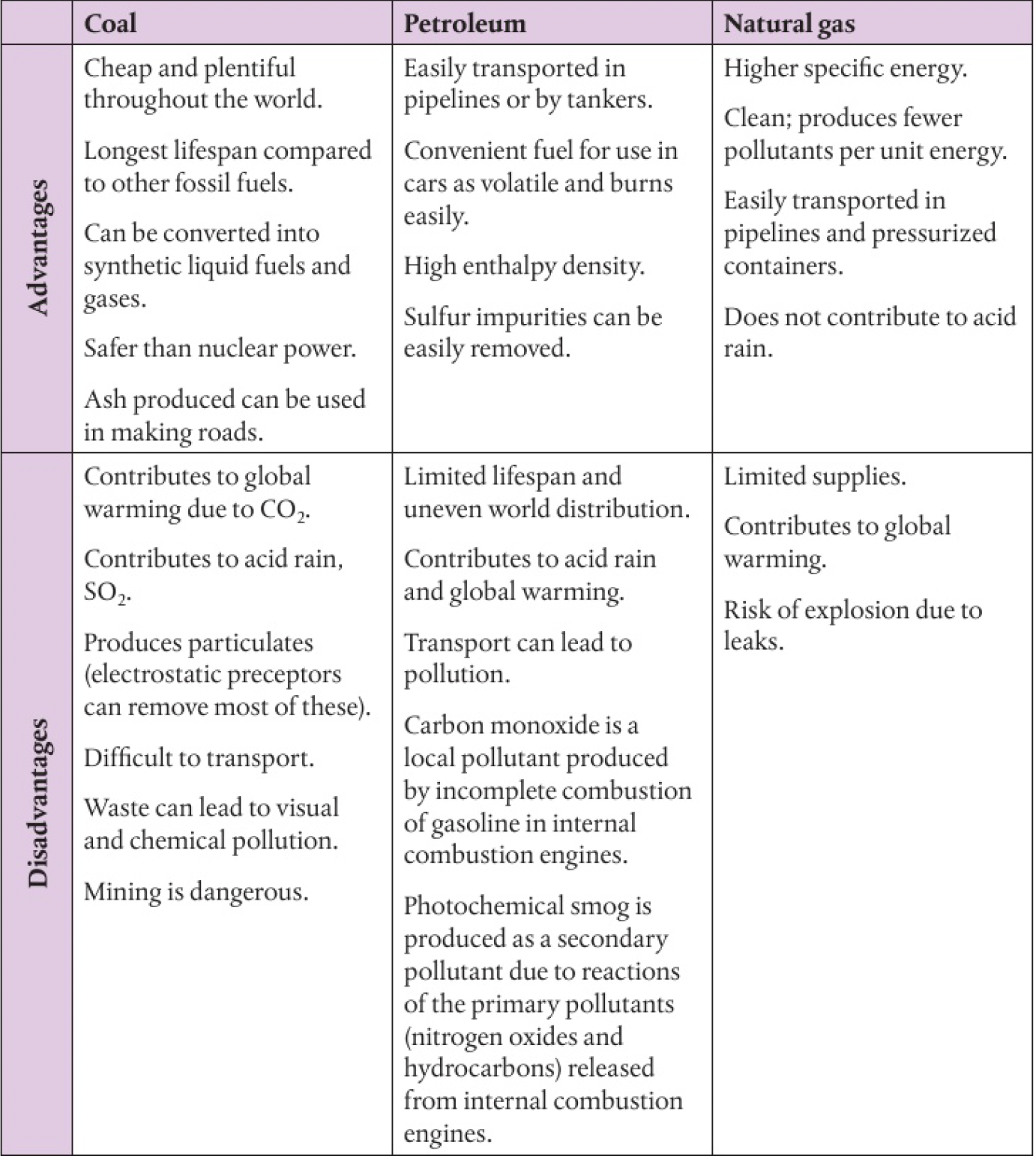
Reactivity 1.3.3 - fossil fuels include coal, crude oil and natural gas, which have different advantages and disadvantages
ideal fuel:
- cheap
- plentiful
- readily accessible
- provides high-quality energy at a reasonable rate
- produce minimal effect on environment
oil currently provides the world’s economy with the most energy
fossil fuels are non-renewable:
- takes millions of years to form
- used at a rate faster than can be replaced
wood is renewable:
- trees can be grown to replace those chopped down
properties
energy density:
- energy produced per unit volume
specific energy:
- energy produced per unit mass
formation
fossil fuels are formed by the reduction of biological compounds. produced by the slow and partial decomposition of plant and animal matter that is trapped in the absence of air. oxygen is lost from the biological molecules at a faster rate than other elements (carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, sulfur), which results in reduced biological compounds which are generally hydrocarbons
coal is the most abundant fossil fuel
- combustible sedimentary rock
- the most plentiful of the earth’s fossil fuels
- anthracite is nearly pure carbon, contains ~80% to ~90% carbon by mass
crude oil
mixture of hydrocarbons:
- straight-chain saturated alkanes
- branched-chain saturated alkanes
- cycloalkanes
- aromatic compounds
- compounds of nitrogen, oxygen, sulfur
used for:
- transport
- electricity generation
- chemical feedstock for organic compounds
- polymers
- pharmaceuticals
- dyes
- solvents
formation:
- remains of marine animals and plants trapped under layers of rock
- high temperature and high pressure
- organic matter decays without bacteria and oxygen
oil and gas are easier to extract than coal as they are fluids and can be pumped up
natural gas
- mostly methane
- contains impurities nitrogen and sulfur compounds
formation:
- organic matter
- heat, pressure, maybe bacteria
- decomposition of crude oil and coal deposits
- trapped in geological formations by impermeable rock
can occur on its own, dissolved under pressure, or in a layer above oil in a reservoir
can be found associated with coal
- cleanest fossil fuel
- low percentage carbon content
- impurities can be easily removed
- combustion produces minimal amounts of carbon monoxide, hydrocarbons, particulates
past and future considerations
advantages and disadvantages
combustion of alkanes in detail
higher carbon content of compound, greater tendency for incomplete combustion of combustion
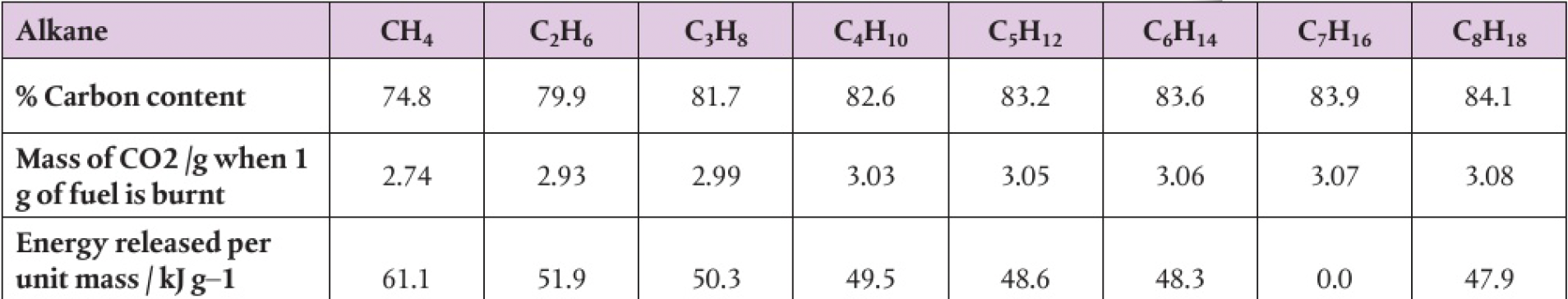
the increase in percentage carbon content down the homologous series suggests that incomplete combustion increases with the length of the carbon chain. this supports the claim that natural gas, is the cleanest of the fossil fuels to burn, and coal, which has a very high carbon content, is the dirtiest
in complete combustion, the mass of carbon dioxide produced per unit mass of fuel increases with the percentage carbon content as well.
the higher the percentage carbon content, the lower the specific energy. the energy obtained per gram of
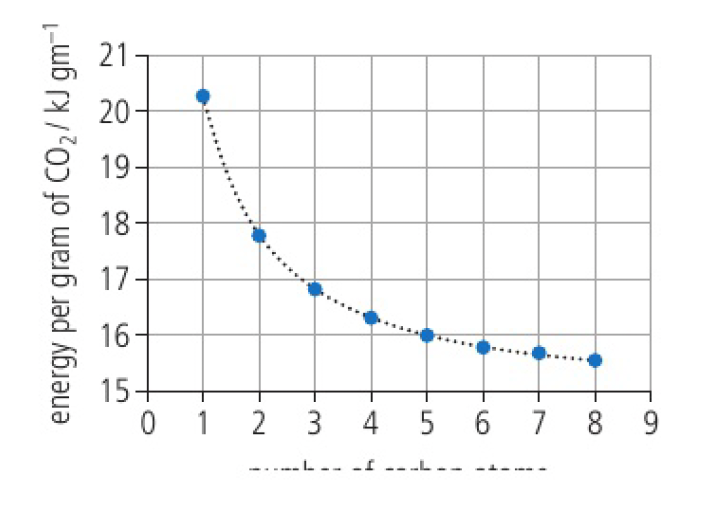
x-axis: number of carbon atoms
the greenhouse effect
greenhouse gases absorb long wave infrared radiation re-radiated from the Earth’s surface
check out 3.2.9 infrared spectroscopy
impact on climate
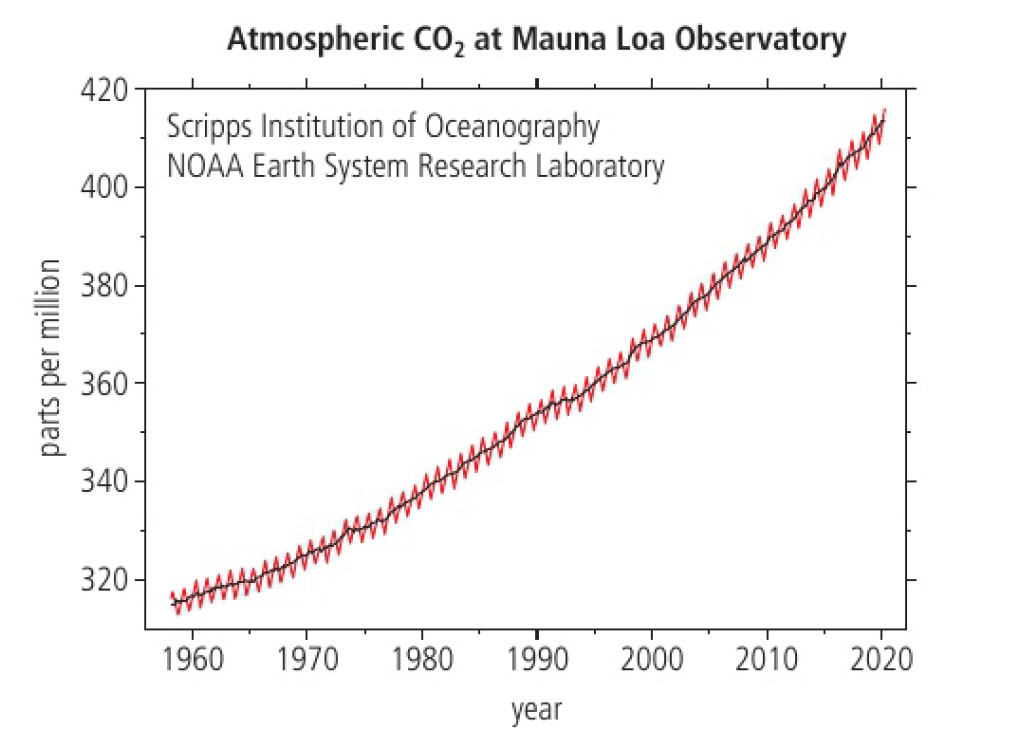
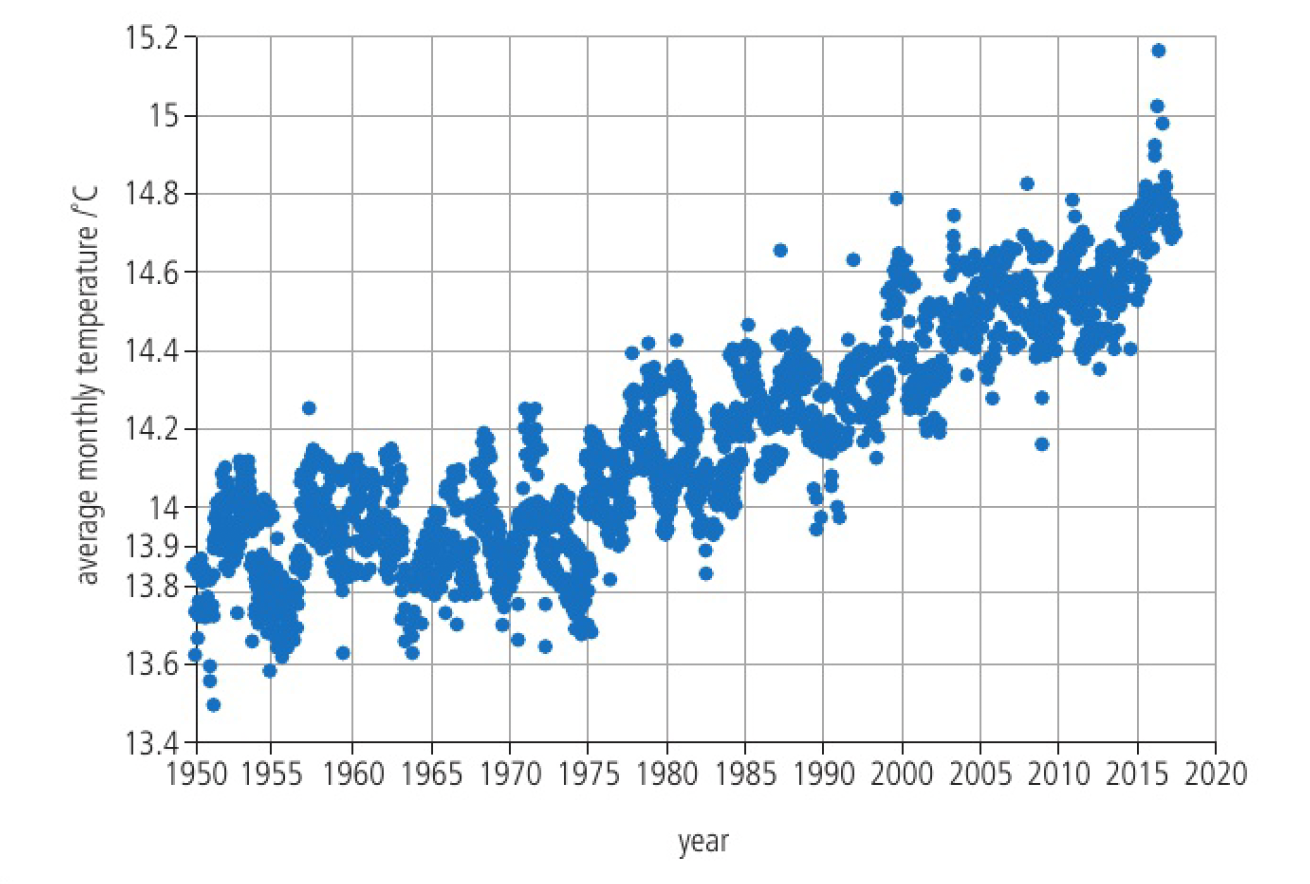
carbon dioxide and other anthropogenic greenhouse gases have increased dramatically. the average temperature of the world has also increased. levels of carbon dioxide will double in about 100 years
the temperature of the Earth could rise by
- changes in agriculture and crop yields
- changes in biodistribution (desertification, loss of cold-water fish habitats)
- rising sea levels (thermal expansion, melting polar ice caps and glaciers)
challenge questions
- on a typical winters day,
of energy is needed in a home. the specific energy densities and approximate empirical formulae of wood and coal and the efficiency of the heating systems are tabulated below.
| fuel | formula of fuel | specific energy | efficiency of heating, % |
|---|---|---|---|
| coal | 31 | 65 | |
| wood | 22 | 70 |
a) calculate the percentage mass of carbon in the two fuels
coal:
wood:
b) determine the carbon footprint from using the two forms of heating in terms of the mass of carbon dioxide produced by the two fuels
coal:
wood:
c) suggest a reason why the carbon footprint calculation for wood does not give a full account of its impact on the environment
in the formation of the wood, carbon was taken out of the environment or that more wood can be grown relatively quickly
a) suggest why the first measurements of
they were remote, distanced from pollution
b) explain the annual fluctuations in
growing plants use
c) identify two different means by which
photosynthesis and solvation in water
$$
\begin{align}
&\ce{6CO_{2} +6H_{2}O\to C_{6}H_{12}O_{6} +6O_{2}} \
&\ce{CO_{2}(g) +H_{2}O(l)\to H_{2}CO_{3}(aq)}
\end{align}