chem whatarethemechanismsofchemicalchange
Reactivity 3.2.9 - functional groups in organic compounds may undergo oxidation
oxidation of alcohols
-
combustion (breaks carbon chain)
-
selective oxidation of the carbon atom attached to the
group (keeps chain intact) -
commonly, acidified potassium dichromate(VI) is used.
-
the oxidising agent is sometimes shown as
the degree of oxidation can be related to the number of
primary alcohols
- 2
atoms attached to carbon with hydroxyl group - can be oxidised in a two-step reaction
CCO>>CC=OCC=O>>CC(=O)O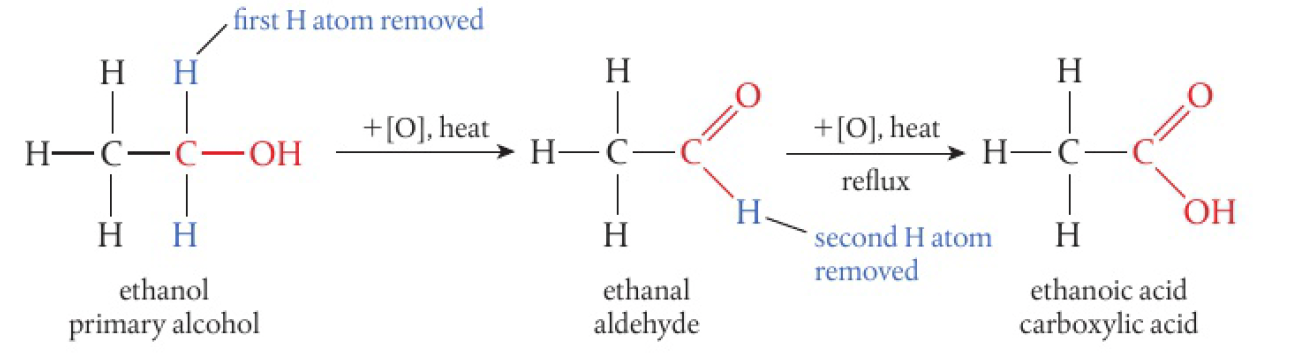
it is possible to remove the aldehyde product by distillation. aldehydes do not have hydrogen bonding, unlike the alcohol or the acid.
the reaction mixture is heated under reflux, meaning the aldehyde condenses back into the reaction mixture when it evaporates.
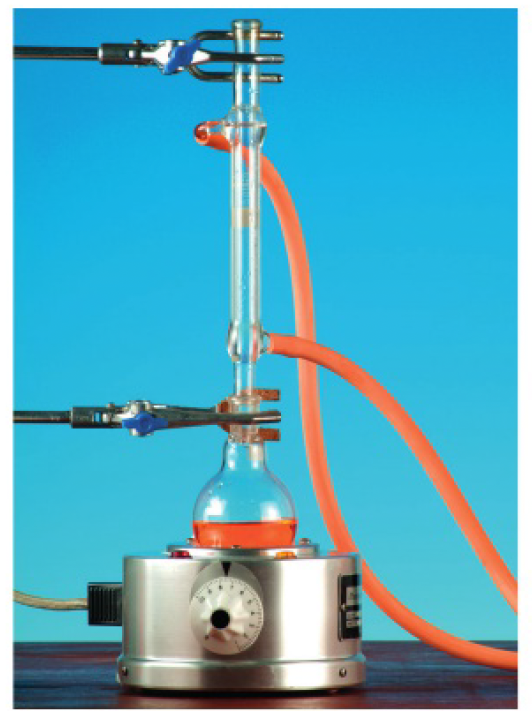

- electric heating mantle
- vapour condenses back into the reaction vessel
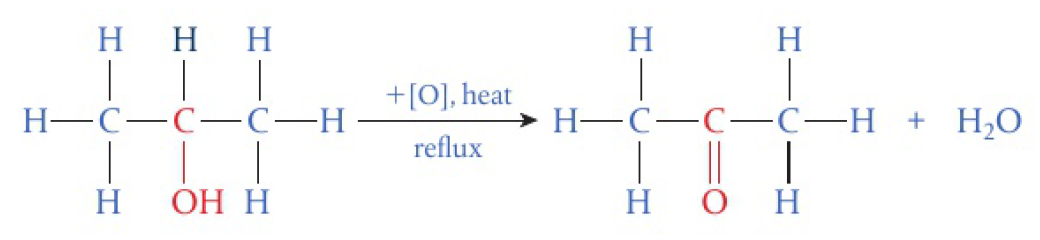
secondary alcohols
- one
- oxidised to ketones
CC(O)C>>CC(=O)C.[H]O[H]tertiary alcohols
- no
- not readily oxidised without breaking the carbon chain
challenge questions
- use oxidation numbers to show the differences in the extent of oxidation in the complete combustion of propane,
propane:
propene:
combustion of propane involves a bigger change of oxidation state and more oxygen is needed
- deduce the half-equations of oxidation and reduction for oxidation of ethanol to produce ethanal with acidified potassium dichromate(VI) and state the overall reaction
oxidation:
reduction:
overall: