Structure 3.1.5 - metallic and non-metallic properties show a continuum. this includes the trend from basic metal oxides through amphoteric to acidic non-metal oxides
see 2.4.1 the bonding triangle
bonding of period 3 oxides
- ionic compounds are generally formed between metal and non-metal elements
- the oxides of elements
to have giant ionic structures
covalent compounds are formed between non-metals, so the oxides of phosphorus, sulfur, and chlorine are molecular covalent
the oxide of silicon (which is a metalloid) has a giant covalent structure
the ionic character of a compound depends on the difference in electronegativity
the conductivity of the molten oxides gives an experimental measure of their ionic character
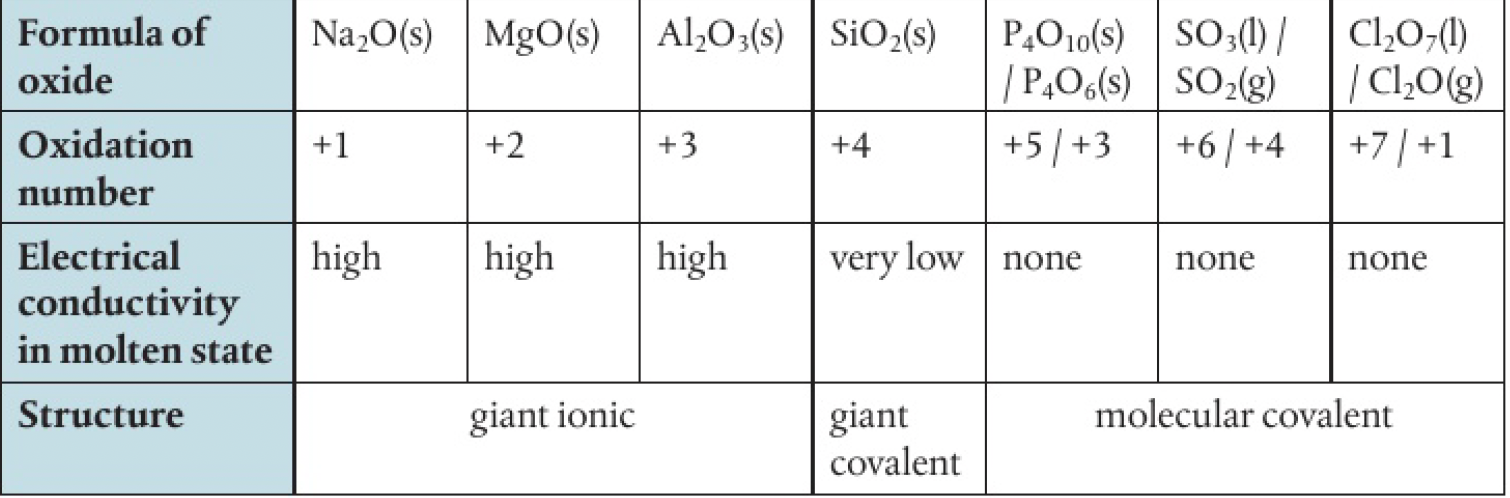
acid-base character of the period 3 oxides
metallic elements, which form ionic oxides, are basic. eg
non-metal oxides, which are covalent, are acidic. eg
aluminium oxide, which can be considered as an ionic oxide with covalent character, shows amphoteric properties - reacting with both acids and bases
behaves as a base when with sulfuric acid
behaves as an acid when reacting with sodium hydroxide
acid rain and acid deposition are produced by non-metal oxides
all rainwater is acidic due to dissolved carbon dioxide in the form of carbonic acid
acid deposition is broader than acid rain and includes all processes by which acidic components as precipitates or gases leave the atmosphere
- wet acid deposition: rain, snow, sleet, hail, fog, mist, dew
- dry acid deposition: dust and smoke that later dissolve in water to form acids
sulfur oxides produce acid rain
- burning fossil fuels, particularly coal and heavy oil (~50% of annual global emissions from coal)
- smelting to extract metals from ores
sulfur dioxide dissolves in rainwater to form sulfuric (IV) or sulfurous acid
sulfur dioxide can be oxidised to sulfur trioxide and dissolve in rainwater to form sulfuric (VI) acid
nitrogen oxides produce acid rain
a similar reaction gives rise directly to nitrogen dioxide
nitrogen dioxide also form from the oxidation of nitrogen monoxide
nitrogen dioxide dissolves in rainwater to form a mixture of nitric (III) or nitrous acid and nitric (V) acid
nitrogen dioxide can also be oxidised to form nitric (V) acid
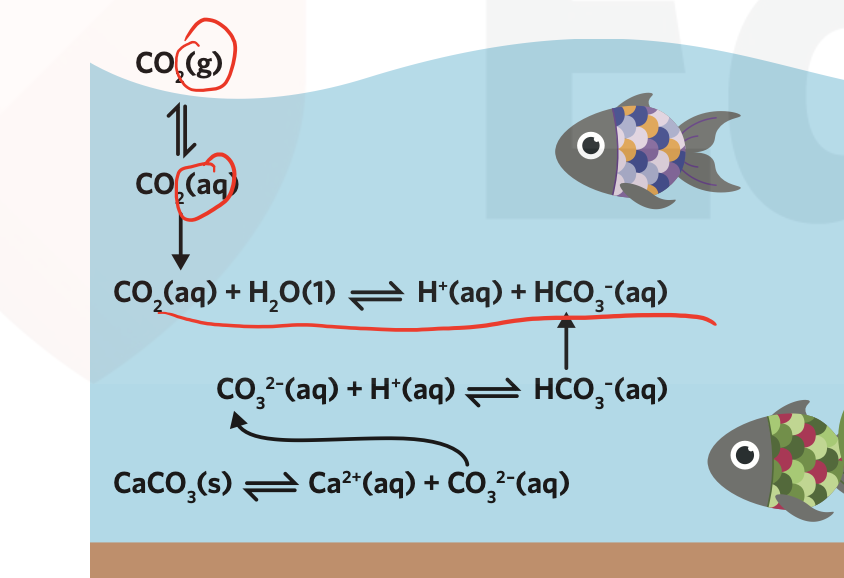
ocean acidification occurs as carbon dioxide dissolves in the oceans
- 50% of carbon dioxide produced by combustion of fossil fuels is dissolved by the oceans
this leads to higher ocean acidity, mostly near the surface, where
- ocean acidity inhibits shell growth and is suspected to be a cause of reproductive disorders in some fish
marine invertebrates use calcium ions and carbonate ions to form shells to protect themselves
challenge questions
- what is the source of sulfur in fossil fuels? consider why some fuels such as coal contain higher amounts of sulfur.
coal and oil are fossilised decayed plants or animals, which would have contained amino acids. the amino acids methionine and cysteine contain sulfur.
- acid rain damages building materials. limestone is a form of calcium carbonate. deduce an equation for the reaction that accounts for damage to calcium carbonate.
\ce{CaCO_{3}(s) +H_{2}SO_{4}(aq)\to CaSO_{4}(s) +H_{2}O(l) +Co_{2}(g)}