chem whatarethemechanismsofchemicalchange
Reactivity 3.2.8 - an electrolytic cell is an electrochemical cell that converts electrical energy to chemical energy by bringing about non-spontaneous reactions
- a voltaic cell takes the energy of a spontaneous redox reaction and harnesses it to generate electrical energy
- an electrolytic cell uses an external source of electrical energy to bring about a non-spontaneous redox reaction
- electricity used to break down substances
the electrolyte is a liquid, usually a molten ionic compound or an aqueous solution of an ionic compound
as electric current passes through the electrolyte, redox reactions occur at the electrodes, removing the charges on the ions and forming electrically neutral products. the ions are discharged
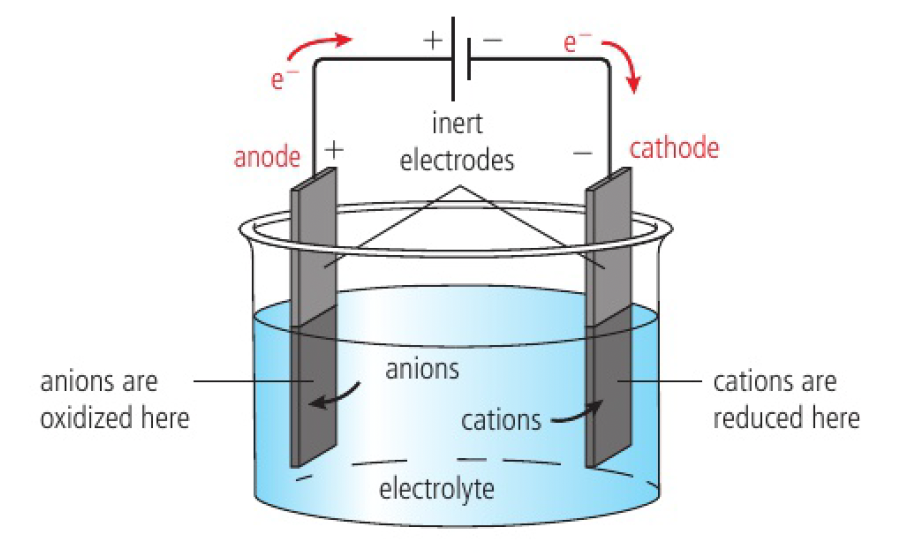
- the source of electric energy is a battery or a DC power source
- the longer line represents the positive terminal
- the electrodes are made from a conducting substance
- they are inert as they do not take part in the redox reactions
- they cannot touch, otherwise the circuit would be shorted
- electric wires connect the electrodes to the power supply
reversing the natural direction of change
- the reaction between
and to produce is spontaneous - electrons are transferred from the sodium to the chlorine
- sodium and chlorine ions are formed which bond to form a
lattice
this process can be reversed if solid
- the ions are mobile and act as an electrolyte if placed in an electrochemical cell
the battery pushes electrons towards the cathode, where they are accepted by
electrons are released at the anode as chlorine ions are oxidised
the released electrons move toward the positive terminal of the DC power source
overall reaction:
the chemical reactions occurring at each electrode remove the ions from the electrolyte, separating the mixture of molten ions
electrolysis of molten salts
-
positive ions are reduced and gain electrons at the cathode
-
negative ions are oxidised and lose electrons at the anode
-
generally involves high temperatures since ionic compounds have high melting points
challenge questions
- explain with chemical equations why the carbon anodes used in the electrolysis of aluminium oxide need to be replaced at regular intervals.
- cryolite is added to molten aluminium oxide to increase its conductivity. explain the low conductivity of aluminium oxide.
aluminium oxide has covalent character. see 2.4.1 the bonding triangle