chem modelsofbondingandstructure
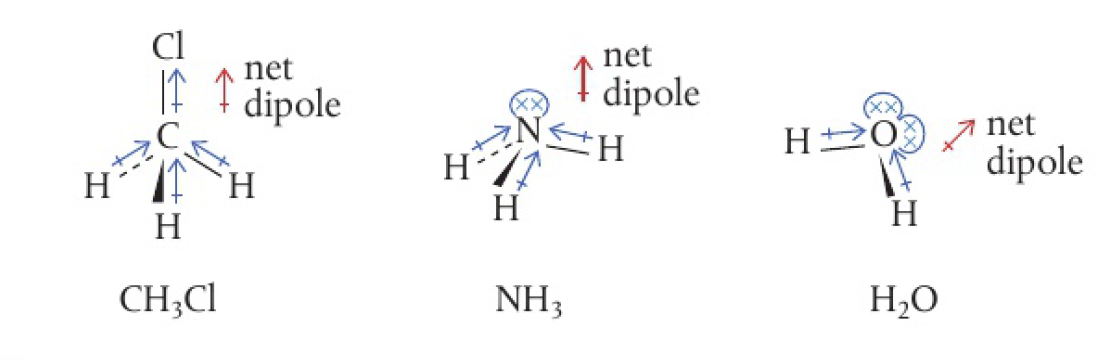
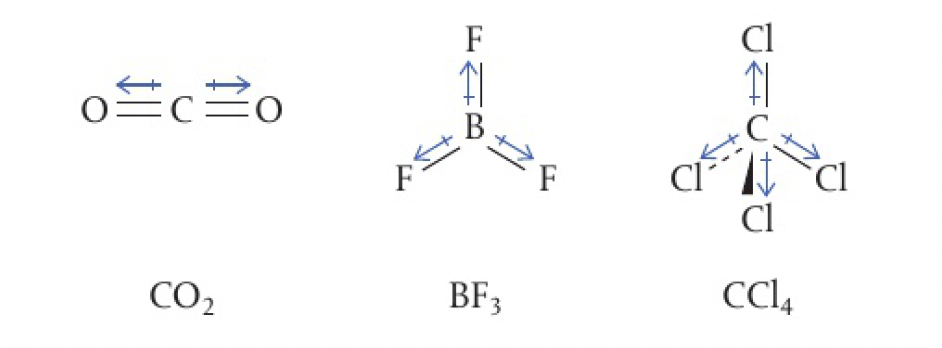
Structure 2.2.6 - molecular polarity depends on both polarity and molecular geometry
in a molecule, if bonds are of equal polarity and are arranged symmetrically with respect to each other, their charge separations will oppose each other and cancel out. this results in a non-polar molecule despite containing polar bonds.
e.g.:
if either the molecule contains bonds of different polarity, or its bonds are not symmetrically arranged, then the dipoles will not cancel out.
e.g.: