Reactivity 2.1.2 - the mole ratio of an equation can be used to determine:
- the masses and/or volumes of reactants and products
- the concentrations of reactants and products for reactions occurring in solution
chemical equation is an expression of reactants combining in a fixed ratio to form products. the most convenient way to express this ratio is as moles.
see 1.4.1 the mole as the unit of amount
the mole ratio of an equation can be used to determine the volumes of gaseous reactants and products.
where
all gases under the same conditions have the same molar volume,
at STP, 0
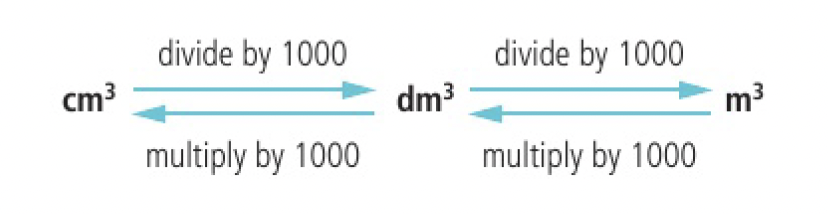
the mole ratio of an equation can be used to determine the concentrations of reactants and products in solutions
can be used in volumetric analysis and titrations
back titrations
back titration is done in reverse by returning to the end point after it is passed. back titration is used when the end point is hard to identify or when one of the reactants is impure.
a known excess of one of the reactants is added to the reaction mixture, and the unreacted excess is then determined by titration against a standard solution. by subtracting the amount of unreacted reactant from the original amount used, the reacting amount can be determined.
challenge questions
- the combustion of both ammonia,
, and hydrazine, , in oxygen gives nitrogen and water only. when a mixture of ammonia and hydrazine is burnt in pure oxygen, the volumetric ratio in the product gas is . calculate the % by mass of ammonia in the original mixture. what assumptions are being made here?
52%