chem modelsofbondingandstructure
Structure 2.1.3 - ionic compounds exist as three-dimensional lattice structures, represented by empirical formulas
ionic lattices are regularly repeating, based on a repeating unit or unit cell that can grow indefinitely. ionic compounds do not have a fixed number of ions, so their formulas are ratios of ions present - empirical formulas, known as the formula unit
the term coordination number is used to express the number of ions that surround a given ion in the lattice. ie for sodium chloride, each
properties
lattice enthalpy as a measure of the strength of the ionic bond
energy is needed to separate particles that are attracted to each other, and energy is released when particles come together.
when one mole of sodium ions forms a lattice with one mole of chloride ions, 790kJ of energy is given out. as the energy content of the chemical species decreases, this is expressed as a negative enthalpy change
this energy output offsets the energy needed to form the ions and makes the formation of the compound energetically feasible
the lattice enthalpy is defined as the enthalpy change for the reverse process. energy is needed to separate the ions and the enthalpy change is positive.
this can be calculated from the ionic model, which assumes that the crystal is made up of spherical ions which only interact by electrostatic forces
the energy needed to separate two ions is proportional to the product of the ionic charges and inversely proportional to the sum of the ionic radii.
- where K is a constant for a structure that takes account of the many ion interactions and depends on the geometry of the lattice
- n and m are magnitude of charges on the ions
and are the ionic radii
this means that:
- increase in ionic charge increases ionic attraction and lattice enthalphy
- increase in ionic radius decreases ionic attraction and lattice enthalpy
- lattice enthalpy is greater for ions with larger charge density as they have a small radius and are highly charged
high melting points & boiling points
the lattice structure results in ionic compounds being crystalline solids at room temperature. they have high mp and bp as a large amount of energy is needed to separate the ions in the lattice.
consider the ionic charge and the ionic radius when comparing melting and boiling points
volatility
volatility is a term used to describe the tendency of a substance to vaporise. ionic compounds also generally have high boiling point sand are non-volatile with low volatility.
solubility
solubility refers to the maximum amount of solute that can dissolve in a given volume. since water is a polar molecule, there are small partial positive charges on the hydrogen and small negative charges on the oxygen that can attract the anions and cations of ionic substances.
the attraction of the ions to the partial charges pulls the ions away from the lattice positions. then, this salt is said to be hydrated. for other solvents other than water, the solute ions are said to be solvated
if the liquid is non-polar, then there is no attraction between the liquid molecules and the ions. ionic compounds are soluble in polar liquids but insoluble in non-polar liquids.
electrical conductivity
the ability of an ionic compound to conduct electricity depends on the freedom of movement of the ions. solids no, liquids/aqueous yes
brittle
crystals shatter when a shear force is applied. the force displaces some ions, resulting in ions of the same charge being positioned alongside each other
deviations
the ionic character of the other halides decrease across a period.
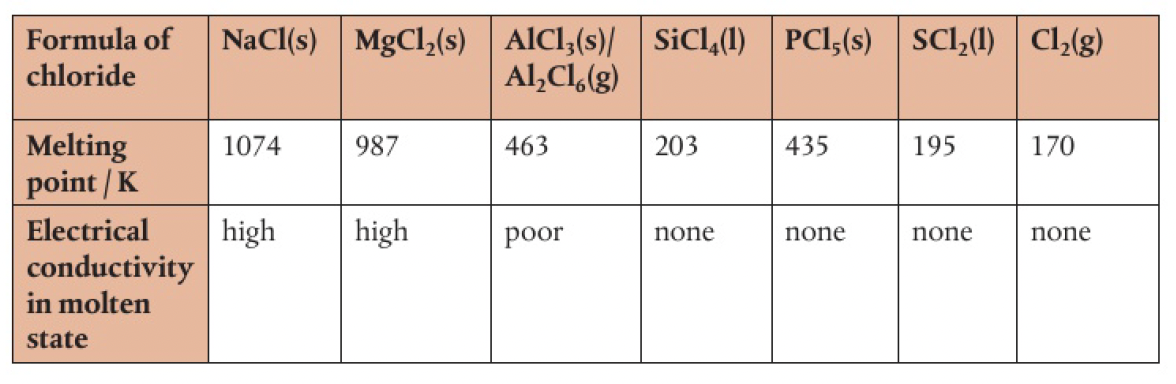
the transition from ionic to covalent character can be seen here.
is considered to be covalent, illustrated by its low conductivity in the liquid state - the move from ionic to covalent is also seen in the decrease in melting points
- aluminium chloride has a layer structure as a solid, but exists as a dimer in liquid and gaseous states
the difference between theoretical lattice enthalpies based on the ionic model and experimental values can be used to measure the covalent character of chlorides
ionic character
this can be quantified using the Pauling scale of electronegativity
a difference of electronegativity of 1.6 corresponds to 50% ionic character. a difference of 1.8 is often taken as corresponding to predominantly ionic
bonding continuum

challenge questions
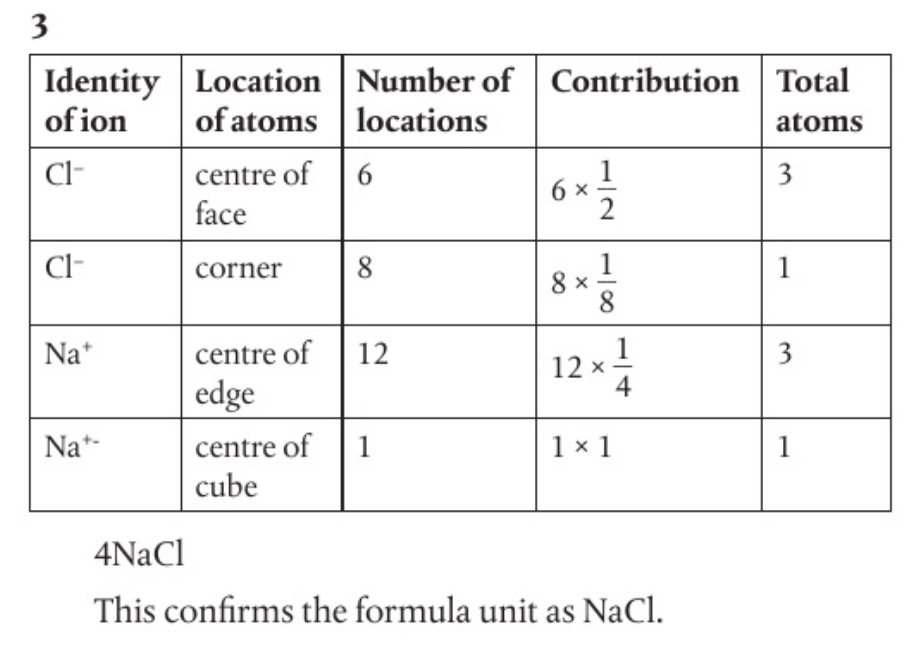
- consider the figure below, which shows one unit cell of the sodium chloride structure.
- each chloride ion on the corner of the cube is a member of eight other unit cells so contributes ⅛ of an ion to each of the eight unit cells.
- each chloride ion on the face of one face is shared by two unit cells and contributes ½ of an ion to both of these unit cells.
- each sodium ion at the centre of an edge is shared by four unit cells and so contributes ¼ of an unit to four unit cells
- there is a sodium ion at the centre of the cube which belongs exclusively to one unit cell and so contributes one ion.
deduce the formula of one unit cell and confirm the formula unit to be NaCl.
- we explained that the higher melting point of magnesium fluoride compared to sodium fluoride is due to the ionic charge of the
ion. explain why this explanation is incomplete.
the
- the melting points of aluminium fluoride and oxide are shown in the table. compare the melting points with the corresponding magnesium compounds and explain any differences.
| ionic compound | charge on metal ion | charge on non-metal ion | melting point / K |
|---|---|---|---|
| aluminium fluoride has a higher melting point due to the increased charge of the aluminium cation |
aluminium oxide has a lower melting point than magnesium oxide, suggesting that there is some covalent character
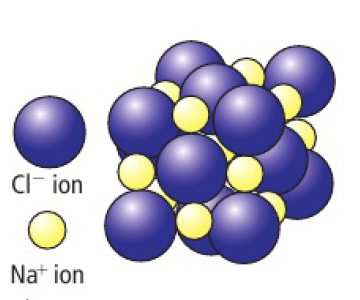
- discuss the usefulness of the model above in describing the real structure of sodium chloride. compare it with the models pictured earlier in the chapter and consider which you think may be the best model.
- the model shows the cubic structure clearly
- the bonds are depicted as lines, but they are electrostatic so in all directions
- the model shows the ions as separated, but in real structure they fill most of the volume