chem whatdriveschemicalreactions
Reactivity 1.2.1 - bond-breaking absorbs and bond-forming releases energy
the bond enthalpy is the energy needed to break one mole of bonds in gaseous molecules under standard conditions
the enthalpy change is positive as it is an endothermic process
for molecules which contain more than 2 atoms, it is more complicated. more energy is needed to break the 1st
similarly, the energy needed to break the
as there are two
all bond enthalpies refer to reactions in the gaseous state, so enthalpy changes resulting from the formation or breaking of intermolecular forces are not included
bond enthalpy and polarity
comparing the average bond enthalpy of the
| X | average of | difference between average and | |
|---|---|---|---|
| +431 | 92 | ||
| +366 | 51.5 | ||
| +298 | 4.5 |
the difference in bond enthalpies between the hydrogen halide bonds and the average bonds in the corresponding elements is greatest with chlorine and smallest with iodine. these differences can be related to the polarity of the molecule. the more polar, the larger the difference. generally, the polar
bond formation
the same amount of energy is absorbed when a bond is broken as is given out when the same bond is formed
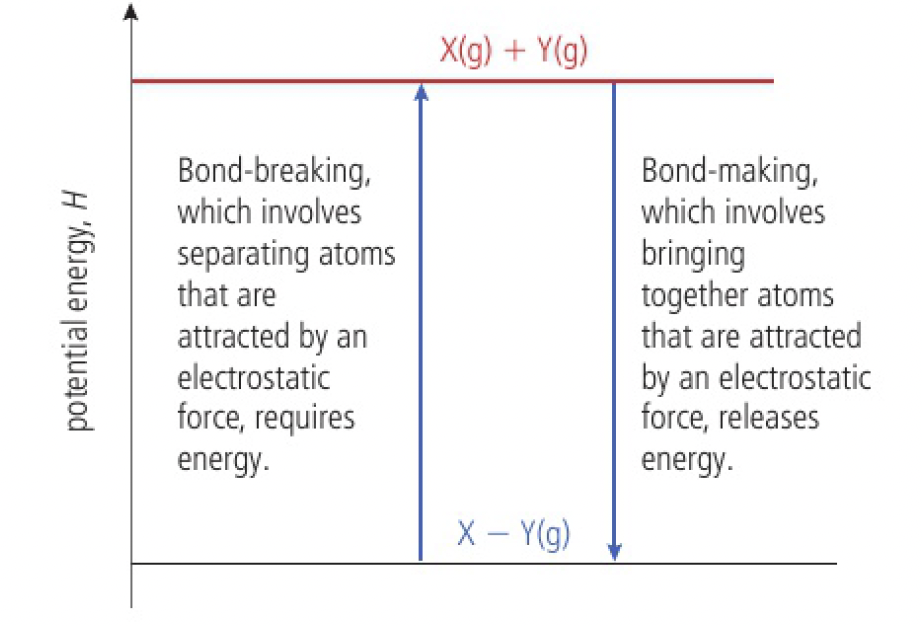
energy changes in reactions
if the bonds formed are stronger than the bonds broken, the reaction is exothermic
challenge questions
-
fluorine shows some anomalous properties due to its small atomic radius
a) comment on the bond enthalpy ofcompared to the bond in the other halogens lower than
and due to the repulsion between the non-bonding pairs in the two fluorine atoms and its small atomic radius b) compare the bond enthalpy of
with the average bond enthalpies of and the difference is
, showing that the bond is very polar and that is very electronegative -
compare the value of the enthalpy of combustion of methane obtained in the worked example to that in Section 14 of the data booklet and estimate the strength of a hydrogen bond.
the worked example obtained a value of
the hydrogen bond has a bond enthalpy of around
-
the bond enthalpy in ozone is
a) compare this bond enthalpy with the oxygen-oxygen bond enthalpies tabulated earlier on 455 and comment on its valuethe average value of an oxygen single bond and an oxygen double bond is 321kJ mol, suggesting that the bond is intermediate, between a single and a double bond.
b) explain why ozone can be decomposed by ultraviolet radiation with a longer wavelength than that required to decompose oxygen
ozone exists a resonance hybrid with two equal bonds between the strength of a double and single bond, which is less than the strength of the double bond present in oxygen. therefore, ozone requires less energy, longer wavelength, to decompose compared to oxygen.