Reactivity 2.3.1 - a state of dynamic equilibrium is reached in a closed system when the rates of forward and backward reactions are equal
physical systems
consider when liquid bromine is placed in a sealed container at room temperature - a closed system:
- bromine is a volatile liquid with a boiling point close to room temperature
- a lot of bromine molecules will have enough energy to vaporise
- since the container is sealed, the bromine vapour cannot escape and its concentration will increase
- some vapour molecules will lose energy and become liquid again
- once the rate of condensation is equal to the rate of evaporation
- there will be no net change in the concentration of either the liquid or the gas. then, the system has reached equilibrium.
chemical systems
consider the reaction of dissociation of
- at the start, there will only be hydrogen iodide in the container
- then, there will be an increase in the purple colour
- in time, the increase in colour will stop
- here, the system has reached equilibrium with the forwards and backwards rate of reaction equal
- the equilibrium is described as dynamic as both forward and backward reactions are still occurring despite their concentrations remaining constant
the equilibrium mixture is when point when the concentration of the reactants and products in a reaction mixture remains constant.
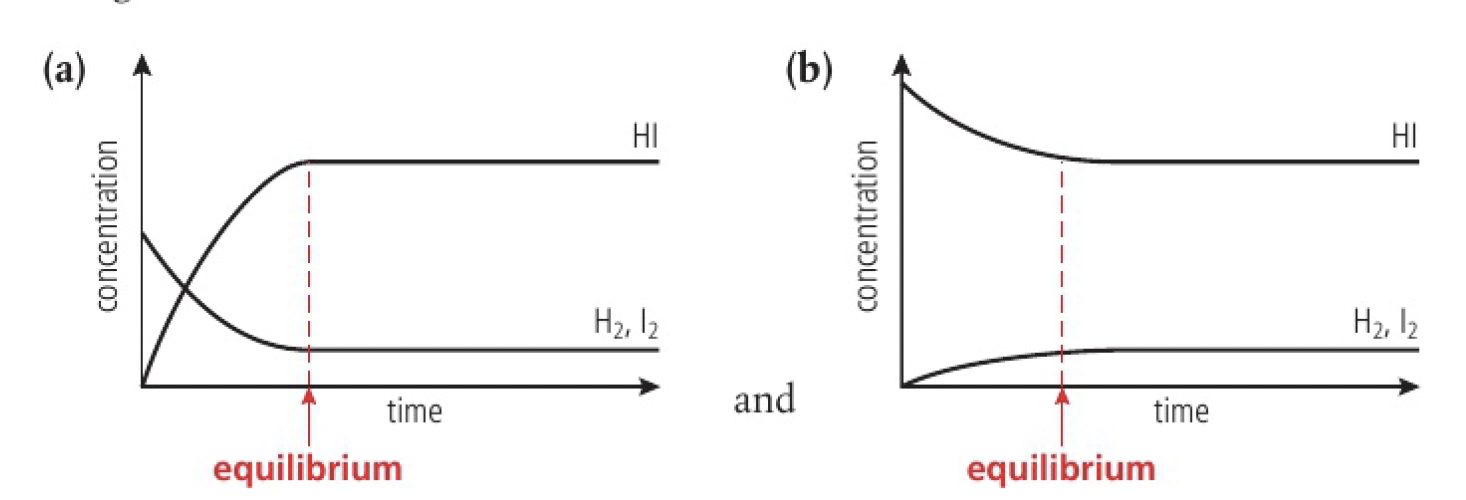
the same equilibrium mixture is reached whether starting from a mixture of the reactants or products.
| characteristics of a physical and chemical system at equilibrium | explanation | |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | equilibrium is dynamic | the reaction has not stopped, but both forward and backward reactions are still occurring at the same rate |
| 2 | equilibrium is achieved in a closed system | a closed system has no exchange of matter with the surroundings, so equilibrium is achieved where both reactants and products can react and recombine with each other |
| 3 | the concentrations of reactants and products remain constant at equilibrium | they are being produced and destroyed at an equal rate |
| 4 | at equilibrium there is no change in macroscopic properties | macroscopic properties are observable properties such as colour and density. these do not change as they depend on the concentrations of che components of the mixture |
| 5 | equilibrium can be reached from either direction | the same equilibrium mixture will result under the same conditions, no matter where the reaction is started with all reactants, all products, or a mixture of both |
- the proportion of reactant and product in the equilibrium mixture is referred to as the equilibrium position
- reactions where the mixture contains mostly products are said to *lie to the right
- reactions where the mixture contains mostly reactants are said to lie to the left
challenge questions
- a closed system is defined differently in different disciplines. in thermodynamics, it means that no matter can be exchanged with the surroundings, but energy can flow. to what extent can the Earth be considered a closed system?
earth receives energy from the Sun and disperses energy, largely as heat. the exchange of matter is minimal. the exceptions to earth being a closed system are matter received from space, such as asteroids and space dust, and matter lost to space, such as spacecraft