chem whatdriveschemicalreactions
Reactivity 1.2.2 - Hess’s law states that the enthalpy change for a reaction is independent of the pathway between the initial and final states
provided the starting conditions and final conditions, reactants and products, are the same
Hess’s law is a consequence of the law of conservation of energy, otherwise it is possible to create and destroy energy
see 1.2.5 Born-Haber cycles (HL)
application of hess’s law
hess’s law allows the enthalpy changes of reactions that cannot be measured in the laboratory to be calculated.
although carbon and hydrogen do not combine directly to form propane, the enthalpy change of the below reaction can be calculated
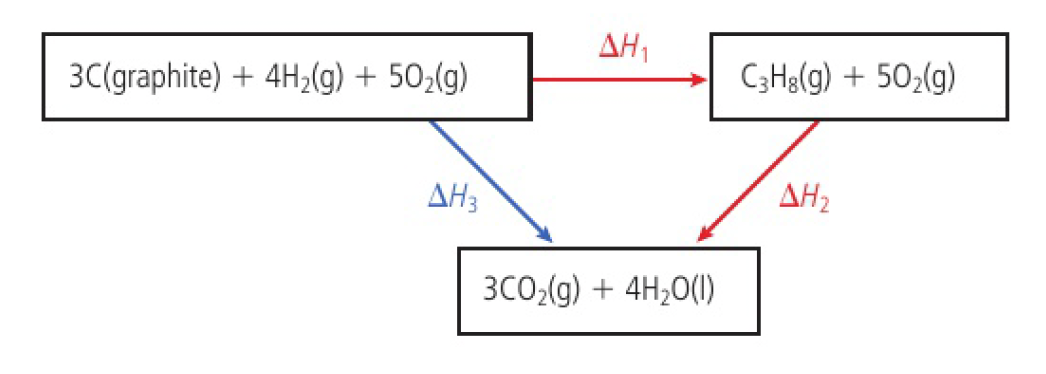
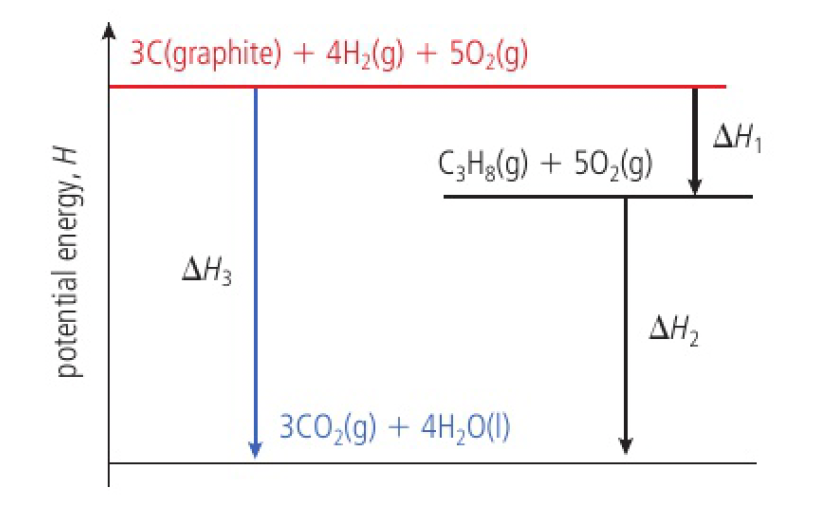
the steps in an enthalpy cycle can be hypothetical, the only requirement being that the individual chemical reactions balance.
challenge questions
- explain why it is difficult to determine the enthalpy change of thermal decomposition reactions directly
the compounds must be heated for reaction to occur. it is difficult to distinguish energy change due to the reaction from the heat input.